The Election Commission of India has taken massive strides in ensuring inclusivity and accessibility in the General Elections 2024 to ensure that no eligible voter is deprived of their right to vote on account of physical or other barriers. So far, after the conclusion of 6 phases of elections, immense enthusiasm was seen amongst voters of various sections such as Persons with Disabilities, Senior Citizens, Transgenders, PVTGs. Facility for voting from the comfort of home for senior citizens above 85 years of age and PwDs with 40% benchmark disability was extended for the first time on pan India basis in General Elections 2024.
Lambada Tribe at Polling Station of Thiruvur Constituency, Shompen tribe of Great Nicobar voted for the first time in a General Election and Nishi Tribe in Arunachal Pradesh
The concerted efforts, throughout the country under the leadership of Chief Election Commissioner Shri Rajiv Kumar along with Election Commissioners Shri Gyanesh Kumar and Dr Sukhbir Singh Sandhu have seen many success stories from the States/UTs where election has been completed till the Phase 6 of the Lok Sabha Election – 2024. CEC Rajiv Kumar said “It has been the deep founded resolve of the Commission to strive for continuous improvement in the electoral processes setting new standards globally. ECI is determined to make the elections truly reflective of the spirit of plurality and diversity that is the pride of our country. ECI is dedicated to incorporating and deeply integrating the principles and practices of inclusivity and accessibility throughout the entire election process, setting an example before the society for replication everywhere.”

A senior citizen elector on the way to cast her vote in Arunachal Pradesh.
The preparations started two years back with concerted efforts of updation and registration of eligible citizens in the electoral rolls. This was achieved by conducting special registration drives, camps, targeting these categories of voters. ECI has adopted a multipronged strategy to enhance participation amongst communities which are prone to be deprived of their right to vote.
Optional home-voting facility: a first in India’s General Elections draws excellent response
The optional home voting facility marks a paradigm shift in the electoral process and has been made available for the first time in the history of India’s general elections. Any eligible citizen aged 85 and above or with 40% benchmarked disability, can avail the provision of home voting facility through postal ballot in these elections. This facility has received an enthusiastic response from voters. Gratifying scenes of smiling voters and their testimonials voting from the comfort of their homes have flooded social media from all parts of the country. Voting from home takes place with involvement of a full contingent of polling staff and security personnel with secrecy of voting diligently maintained. Agents of candidates are also allowed to accompany polling teams to witness the process.


Smt. D. Padmavathi, 100 years of age, from Kovvuru Constituency and a Sr. Citizen elector from Arunachal Pradesh

Eight PwD members of same family availing home facility in Churu, Rajasthan.
Bridging barriers: addressing infrastructural requirements for better participation
To bridge any infrastructural gaps, ECI ensured that every polling booth is on the ground floor, equipped with assured amenities including ramps, signages for voters, parking space, separate queues, and volunteers. Additionally, ECI’s SAKSHAM app has facilitated PwDs for availing various facilities at polling station like wheelchairs, pick-and-drop and volunteers services. There have been over 1.78 lakh downloads of the Saksham App since announcement of elections.
The Commission has also made provisions for Braille on EVMs, Braille enabled EPIC, and voter slips to assist visually impaired electors. Further, a Voter Guide for PwDs and Sr. Citizens, in English and Hindi, with information on the process of registration to poll day facilitation was made available.
|

In Indore, Madhya Pradesh, 70 visually handicapped girls were assisted with free transportation to cast their vote.
|

PwD managed PS in J&K
|




Braille enabled EPIC, Voter Guide, volunteer at a polling station in Bihar and provision of shamiyana at a polling station in Odisha
Inclusivity in spirit: removing psychological barriers to voting
Apart from eradicating physical barriers to voting, ECI also made efforts to address social barriers and stigma surrounding certain vulnerable populations like Transgenders, Sex workers, PVTGs to ensure their participation in election process. Special camps were arranged to enroll the third gender (TG) electors and other marginalized communities like sex workers and PVTGs by Thane District in collaboration with civil society. Over 48,260 TGs are enrolled all over the county, out of which Tamil Nadu has the highest number of third gender electors with 8467, followed by 6628 TGs in Uttar Pradesh and 5720 TGs in Maharashtra.
As part of SVEEP initiatives, Commission organized a T-20 Cricket Match on 16th March, 2024 between the IDCA (Indian Deaf Cricket Association) and DDCA (Delhi District Cricket Association) teams to create voter awareness among PwD electors and promote inclusive elections.

Commission awarding the trophy to the winners at the T-20 Match
Efforts were made to the extent possible by the Commission, to set up at least one polling station in each AC, managed exclusively by PwD officials. For Lok Sabha Election -2024, approximately 2697 PwD managed Polling Stations have been set up across the country, with Uttar Pradesh setting up the highest PwD Manned Polling Stations i.e. 302.
Making registration and voting easy for vulnerable communities
The homeless and other nomadic groups are another critical demographic in achieving high electoral participation. Due to their unique circumstances, these individuals can experience unintentional electoral exclusion because of lack of proof of residency. However, special efforts were made in the last two years for their enrolment as voters and also participation in the voting process. Location of new polling booths in previously inaccessible areas has led to the large-scale inclusion of PVTGs. In many States/UTs, where PVTGs reside in large numbers, free transportation facilities have been provided for enabling the PVTGs reach polling stations from remote areas. In a historic move, the Shompen tribe of Great Nicobar voted in the Lok Sabha Election -2024 for the first time.
To promote electoral awareness and instill a spirit of partnership and inclusion in the elections, ECI has designated eleven PwD individuals as “ECI Ambassadors” to involve the community further in the electoral process. Polling personnel were are also trained and sensitized regarding special needs of the PwDs to develop a sense of participation and ownership in the elections. State CEOs also collaborated with State Disability and health departments of the concerned states for providing better facilitation to PwDs and Senior Citizens.

Camps organized in Gangtok by DEO in collaboration with Women & Child Development and Health Department
Also, a team of ECI officials visited Thane District and Kamathipura in Mumbai City to have an open dialogue with the Transgender and Female Sex workers, residing in these areas, to better understand the challenges faced by them in electoral participation, sensitizing the field machinery towards these electors and to encourage these voters to ensure their participation during the Lok Sabha Election-2024.

ECI team with NGOs/CSOs and TG community in Thane District and encouraging them to ensure 100% participation in the Lok Sabha Election.
The Commission also appointed Ms. Sheetal Devi, Arjuna Awardee and Para Archer, as the ECI National Icon, to motivate the PwD electors to exercise their franchise in the Lok Sabha Election-2024. Also, eleven prominent PwD personalities have been appointed as Ambassadors of ECI for taking part in various voter awareness initiatives of ECI and reaching out to PwD electors. Moreover, the Commission has also appointed State PwD Icons for the States/UTs.
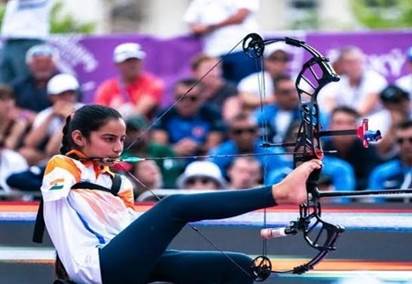
Ms. Sheetal Devi, National PwD Icon, ECI
|

In Mehsana district in Gujarat, a wheelchair rally
was organized by PwD electors to create awareness
|

An extensive campaign including “Matdata appeal patra” was launched to enhance PVTG participation in the ongoing elections.
|
Reaching out to the last mile electors
The Commission is committed in ensuring that “no voter is left behind” and has taken special measures to reach out to the electors residing in the remotest corners of the county. For example, a polling station was set up in a shipping container in Aliabet in Gujarat to reach out to the tribal electors residing in this area. Similarly, voters from 102 villages in Bastar and Kanker PCs in Chhattisgarh cast their vote in a polling booth set up in their own village for the first time in a Lok Sabha Election.

Polling station for just five members of a family in a remote village of Warshi in Leh district, Ladakh
Further, in a major decision to facilitate voting by Kashmiri migrants in the ongoing General Elections 2024, ECI abolished the cumbersome procedure of filling Form-M for the displaced people from the valley who are residing in Jammu and Udhampur. Additionally, for the migrants residing outside Jammu and Udhampur (who will continue to submit Form M), ECI has authorized the self-attestation of the certificate appended with Form-M, thus removing the hassle of getting this certificate attested by the Gazetted Officer. The Commission has enabled Kashmiri migrant voters residing at various relief camps in Delhi, Jammu, and Udhampur to also have the option of voting in person at designated special polling stations or using postal ballot. 21 Special Polling Stations were established at Jammu, 1 at Udhampur and 4 at Delhi.



Kashmiri migrants casting their vote at Special Polling Stations
Similarly, to ensure voting rights for internally displaced persons (IDPs) in Manipur, 94 Special Polling Stations (SPS) were set up in 10 districts for (IDPs). One SPS was set up in Tengnoupal district for a single voter. Poll was conducted under webcasting/videography and displaced persons staying outside relief camps could also opt to vote at SPS.



IDP in Manipur casting their vote at Special Polling Stations
******














































You must be logged in to post a comment.