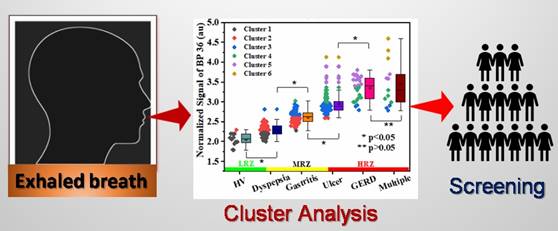
A newly developed non-invasive method of recognising breath patterns can help rapid, one-step diagnosis and classification of various gastric disorders like dyspepsia, gastritis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Currently, peptic ulcer disease is an important medical-social problem that has received special attention all over the world. Helicobacter pylori bacterial infection is considered to be the most significant risk factor for the development of this disease. Patients with peptic ulcer encircling both duodenal and gastric ulcer may remain asymptomatic or symptomatic, and due to undefined risk factors along with lack of specific symptoms at the early stages, the diagnosis is often delayed, leading to poor prognosis and high rates of recurrence of the diseases.
Conventional painful and invasive endoscopic procedures are not suitable for early detection of the acute onset and progression of peptic ulcer as well as various gastric complications. Moreover, the conventional endoscopic methodology is not suitable for general population-based screening and consequently, many common people with complex gastric phenotypes remain undiagnosed.
Prof. Manik Pradhan and his research team at S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, used a pattern-recognition based clustering approach that can selectively distinguish the breath of peptic ulcer and other gastric conditions with that of healthy individuals.
The team used machine learning (ML) protocol to extract the correct information from the large complex breathomics data sets generated from exhaled breath analysis. In a paper published in the European Journal of mass spectroscopy, they implemented the clustering approach to recognize unique breath-pattens, breathograms, and “breathprints” signatures. This helped in a clear reflection of the specific gastric condition of an individual person along with three different risk zones for discrimination of early and late-stage gastric conditions and precise transition from one disease state to another state.
The breath-patterns generated from the patients are irrespective of the patient’s basal metabolic rates (BMR) and other confounding factors such as age, sex, smoking habits, or lifestyle.
The research carried out Technical Research Centre (TRC) at S. N. Bose Centre funded by the DST involved a project student Ms. Sayoni Bhattacharya and project scientists Dr. Abhijit Maity and Dr. Anil Mahato who worked in collaboration with Dr. Sujit Chaudhuri, a renowned medical scientist and Gastroenterologist at AMRI Hospital, Kolkata.
Over the decades, few volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or metabolites in the exhaled breath have been proposed for the non-invasive diagnosis of gastric conditions. However, a particular VOC is related to multiple of clinical surroundings and is likely to be affected by comorbid conditions, suggesting a single molecular marker is not suitable for distinguishing various gastric complications.
Prof. Pradhan who has been working on breath analysis for several years has for the first time unravelled missing links between various gastric conditions and pattern-recognition-based clustering method. These missing links has helped in the non-invasive diagnosis of various gastric disorders through a single breath test without going for painful endoscopy.
The fundamental concept behind the idea was based on the fact that the overall effect of the compounds produced endogenously by various biochemical reactions and intracellular/extracellular processes associated with the pathogenesis of various gastric phenotypes is reflected in the specific masses of the breathprints. Hence the method obviates the necessity of identification of molecular species in exhaled breath for diagnosis and classification of peptic ulcer.
The scientists have developed a prototype device called “Pyro-Breath” clinically validated it in a hospital environment and patented it. The relevant technology has been transferred through NRDC, New Delhi to a startup company for potential commercialization
This can open up new non-invasive avenues for early detection, selective classification, and assessment of progress of various gastric complications and could help widespread population screening of infants, children, pregnant women, and seniors.
Publication link: https://doi.org/10.1177/14690667231174350
For more details, please contact:
Prof. Manik Pradhan (manik.pradhan@bose.res.in)

























You must be logged in to post a comment.