
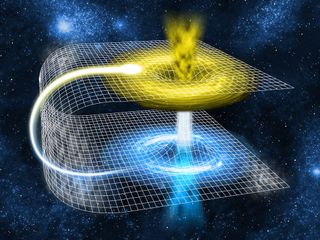
Wormhole theory
Wormholes were first theorized in 1916, though that wasn’t what they were called at the time. While reviewing another physicist’s solution to the equations in Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity, Austrian physicist Ludwig Flamm realized another solution was possible. He described a “white hole,” a theoretical time reversal of a black hole. Entrances to both black and white holes could be connected by a space-time conduit.
In 1935, Einstein and physicist Nathan Rosen used the theory of general relativity to elaborate on the idea, proposing the existence of “bridges” through space-time. These bridges connect two different points in space-time, theoretically creating a shortcut that could reduce travel time and distance. The shortcuts came to be called Einstein-Rosen bridges, or wormholes.
“The whole thing is very hypothetical at this point,” said Stephen Hsu, a professor of theoretical physics at the University of Oregon, told our sister site, LiveScience. “No one thinks we’re going to find a wormhole anytime soon.”
Wormholes contain two mouths, with a throat connecting the two. The mouths would most likely be spheroidal. The throat might be a straight stretch, but it could also wind around, taking a longer path than a more conventional route might require.
Einstein’s theory of general relativity mathematically predicts the existence of wormholes, but none have been discovered to date. A negative mass wormhole might be spotted by the way its gravity affects light that passes by.
Certain solutions of general relativity allow for the existence of wormholes where the mouth of each is a black hole. However, a naturally occurring black hole, formed by the collapse of a dying star, does not by itself create a wormhole.
Through the wormhole
Science fiction is filled with tales of traveling through wormholes. But the reality of such travel is more complicated, and not just because we’ve yet to spot one.
The first problem is size. Primordial wormholes are predicted to exist on microscopic levels, about 10–33 centimeters. However, as the universe expands, it is possible that some may have been stretched to larger sizes.
Another problem comes from stability. The predicted Einstein-Rosen wormholes would be useless for travel because they collapse quickly.
“You would need some very exotic type of matter in order to stabilize a wormhole,” said Hsu, “and it’s not clear whether such matter exists in the universe.”
But more recent research found that a wormhole containing “exotic” matter could stay open and unchanging for longer periods of time.
Exotic matter, which should not be confused with dark matter or antimatter, contains negative energy density and a large negative pressure. Such matter has only been seen in the behavior of certain vacuum states as part of quantum field theory.
If a wormhole contained sufficient exotic matter, whether naturally occurring or artificially added, it could theoretically be used as a method of sending information or travelers through space. Unfortunately, human journeys through the space tunnels may be challenging.
“The jury is not in, so we just don’t know,” physicist Kip Thorne, one of the world’s leading authorities on relativity, black holes and wormholes, told Space.com. “But there are very strong indications that wormholes that a human could travel through are forbidden by the laws of physics. That’s sad, that’s unfortunate, but that’s the direction in which things are pointing.”
Wormholes may not only connect two separate regions within the universe, they could also connect two different universes. Similarly, some scientists have conjectured that if one mouth of a wormhole is moved in a specific manner, it could allow for time travel.
“You can go into the future or into the past using traversable wormholes,” astrophysicist Eric Davis told LiveScience. But it won’t be easy: “It would take a Herculean effort to turn a wormhole into a time machine. It’s going to be tough enough to pull off a wormhole.”
However, British cosmologist Stephen Hawking has argued that such use is not possible. [Weird Science: Wormholes Make the Best Time Machines]
“A wormhole is not really a means of going back in time, it’s a short cut, so that something that was far away is much closer,” NASA’s Eric Christian wrote.
Although adding exotic matter to a wormhole might stabilize it to the point that human passengers could travel safely through it, there is still the possibility that the addition of “regular” matter would be sufficient to destabilize the portal.
Today’s technology is insufficient to enlarge or stabilize wormholes, even if they could be found. However, scientists continue to explore the concept as a method of space travel with the hope that technology will eventually be able to utilize them.
“You would need some of super-super-advanced technology,” Hsu said. “Humans won’t be doing this any time in the near future.”
Additional resources:














/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/1d/94/1d94a50d-2cad-4307-8c01-c337ead1fef9/feb15_j03_antikythera.jpg)






















You must be logged in to post a comment.