Various schemes and Missions run by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs during 2021 have helped boost the Make in India and AtamNirbharBharat initiatives in many ways. The schemes and Missions have directly influenced the AtamNirbhar Bharat and Make in India initiatives directly or indirectly.
Under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U), launched to address urban housing shortage including the slum dwellers by ensuring a pucca house to eligible urban households by the year 2022, the technology used to build the houses at faster speed was innovative, specially the Light House projects as part of Global Housing Technology Challenge – India (GHTC -India) initiative, in six States .The initiative led to a new era in the construction technology in India, thus giving impetus to Make in India initiative. Bringing people and technology together, LHPs will pave the way for a new eco- system where globally proven technologies will be adopted for cost-effective, environment friendly and speedier construction. Advantages of these LHPs are many, the primary ones being durability, climate-resilient, affordability, safety and speed.
MoHUA also launched the Enrolment Module for TECHNOGRAHIS including students from IITs, NITs, engineering, planning and architecture colleges, faculty members, academicians, and stakeholders for registering themselves to visit Live Laboratories at six LHP sites for learning, consultation, generation of ideas and solutions, experimentation, innovation, and technical awareness. This helped them in getting a first-hand account of the technologies being used and in turn, they can adapt and adopt them as per their requirements in the construction sector for a ‘Make in India’ approach.
A Technology Sub-Mission (TSM) was set up to facilitate the adoption of innovative, sustainable, eco-friendly and disaster-resilient technologies and building materials for low-cost, speedier and quality construction of houses. TSM not only aims to ensure speedier and safer delivery under PMAY-U but also has the potential to bring a paradigm shift in the overall housing construction sector in the country.
Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHC) Scheme under Atmanirbhar Bharat Package addresses the vision of ‘AtmaNirbhar Bharat Abhiyan’ significantly by creating a sustainable ecosystem of affordable rental housing solutions and to achieve overall objective of “Housing for All” encompassing the need of affordable rental housing for urban migrants/poor. ARHCs will provide them dignified living with necessary civic amenities near their place of work.
Under Smart Cities Mission(SCM), the City Innovation Exchange (CiX) platform was launched for innovative practices in cities. The platform was a significant addition to the growing innovation ecosystem of India and focuses on fostering innovative practices in cities. CiX, through an ‘open innovation’ process, engages with innovators to design-test-deliver on solutions to pressing urban challenges. This initiative is among the ongoing efforts of the Government to realise Prime Minister’s vision of New and AtmaNirbhar Bharat, by making cities more self-reliant and enabled to meet the needs of and provide services to their citizens. Another step towards making the SCM targets easier, a SmartCode is a platform was launched by MoHUA that enables all ecosystem stakeholders to contribute to a repository of open-source code for various solutions and applications for urban governance. It is designed to address the challenges that ULBs face in the development and deployment of digital applications to address urban challenges, by enabling cities to take advantage of existing codes and customising them to suit local needs, rather than having to develop new solutions from scratch. The India Urban Data Exchange has been developed in partnership between the Smart Cities Mission and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru. A New smart cities website & Geospatial management information system GMIS for project monitoring was also developed to implement and proper scrutiny of the projects under SCM.
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs launched the Transport4All, aiming to bring together cities, citizen groups, and start-ups to develop solutions that improve public transport to better serve the needs of all citizens. It also started the EatSmart Cities Challenge which aimed to motivate Smart Cities to develop a plan that supports a healthy, safe and sustainable food environment supported by institutional, physical, social, and economic infrastructure along with the application of ‘smart’ solutions to combat food related issues.
National Urban Digital Mission will create the ideal space to harness immense synergies from the domain of urban and technology towards creating a citizen-centric governance that reflects Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s vision of ‘minimum government and maximum governance’. The National Urban Digital Mission (NUDM) will create a shared digital infrastructure for urban India, working across the three pillars of people, process, and platform to provide holistic support to cities and towns. It will institutionalise a citizen-centric and ecosystem-driven approach to urban governance and service delivery in 2022 cities by 2022, and across all cities and towns in India by 2024.
For making the street vendors AtmaNirbhar, Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNibhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme, MoHUA has entered into MoU with Zomato, one of the largest online platforms for ordering and delivery of food in India, to onboard street food vendors on its food-tech platform. It has given street food vendors online access to thousands of consumers and help these vendors grow their businesses. Further, MoHUA launched the Mobile Application for PM SVANidhi se Samriddhi- Socio-economic profiling of PM SVANidhi beneficiaries and their families to link them to various Central Government Schemes
Under AtmaNibhar Bharat initiative, DAY-NULM scheme has focussed on equipping the urban poor women with adequate skills and opportunities, and to enable them to promote sustainable micro enterprises. It mobilises women from urban poor households into SHGs and their federations to create a support system for these women. Over 5.7 lakh SHGs have been formed across various States/ UTs, with almost 60 lakh members. Many of these SHGs are engaged in livelihood activities, producing goods such as handicrafts, textiles, toys, eatables and so on. These were being sold primarily in local neighbourhood markets and often faced barriers in achieving visibility and wide market access.
Under Urban Transport Mission, the metro coaches which were earlier imported from Spain, South Korea, and China, are now being manufactured within the country. Their quality is at par with international standards and also being exported to Australia and Canada.
Under the Central Vista project, the new Parliament Building is an intrinsic part of the vision for Azadi@75 and symbolises our commitment and efforts towards building AatmaNirbhar Bharat. The new Parliament has been designed and is being built by Indians using Indian materials. It will be the first Indian Parliament built by the people, of the people, and for the people.
To enable the vision of Hon’ble Prime Minister for New Urban India, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs organised Azadi@75 Conference-cum-Expo in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh along with an exhibition themed on transforming urban landscape across the country.
Achievements and initiatives
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U)
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) was launched on 25th June, 2015 to address urban housing shortage among the EWS/ LIG and MIG category, including the slum dwellers by ensuring a pucca house to eligible urban households by the year 2022.
- Against the total assessed demand of 1.12 Cr houses, 1.14 Cr houses have been sanctioned. Of these, total of 91.5 lakh houses were grounded for construction and 53 lakhs houses were completed / delivered, as on 12th Dec’ 2021.
- A total of 17.35 Lakh beneficiaries have availed subsidy on housing loans through Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme (CLSS), out of which 6.15 Lakh beneficiaries are from Middle Income Group.
- A total of 6,368 houses in Light House Projects are being constructed involving project cost of ₹790.57 crore.
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation & Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Against total SAAP size of ₹77,640 crore, 5818 projects worth ₹80,713 crore have been grounded. Of the grounded projects, works worth ₹57,414 cr. have been physically completed (inclusive of completed projects worth ₹22,756 cr.) and expenditure of ₹50,118 cr. has been incurred so far.
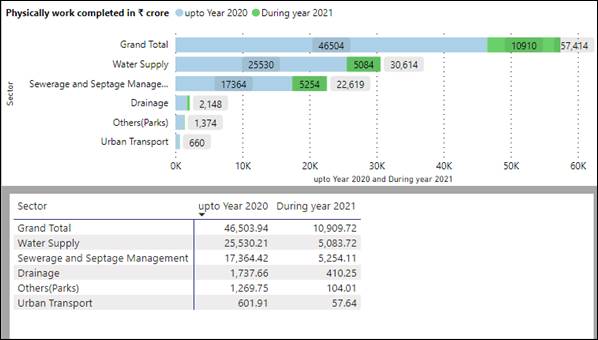
- Sector-wise progress of AMRUT projects is as below:
|
Sector |
Projects completed |
Projects ongoing |
Total Projects Grounded |
|||
|
No. |
Amount |
No. |
Amount |
No. |
Amount |
|
|
Water Supply |
740 |
11,530 |
586 |
30,320 |
1,326 |
41,850 |
|
Sewerage &Septage |
370 |
8,259 |
483 |
25,074 |
853 |
33,332 |
|
Storm Water Drainage |
612 |
1,114 |
187 |
1,829 |
799 |
2,943 |
|
Non-motorised urban transport |
218 |
397 |
131 |
626 |
349 |
1,023 |
|
Parks & Green spaces |
1,943 |
1,130 |
548 |
435 |
2,491 |
1,565 |
|
Total |
3,883 |
22,430 |
1,935 |
58,284 |
5,818 |
80,713 |
- AMRUT 2.0 was launched by the Hon’ble Prime Minister on 1st October 2021 with the aim of making the cities ‘water secure’ and providing functional water tap connections to all households. The total indicative outlay for AMRUT 2.0 is ₹2,77,000 Cr including central share of ₹ 76,760 Cr for the period from 2021-22 to 2025-26.In the water supply sector, contracts for 1,326 projects worth ₹41,850 crore have been awarded of which 740 projects worth ₹11,530 crore have been completed. In addition, 18 projects worth ₹358 crore are at various stages of tendering. The target is to provide 139 lakh water tap connections to achieve universal coverage. So far 118 lakh water tap connections have been provided through AMRUT and in convergence with schemes.
Swachh Bharat Mission- Urban (SBM-U)
Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban) was launched on 2nd October 2014, with the vision to make India open defecation free. Under the mission, 31 cities have been self-declared as ODF and 58 have been certified as ODF since 1st January 2021. ODF+ certified cities increased by 1,828 and ODF++ certified cities increased by 472 since 1st January 2021. Number of Individual Household toilets constructed increased by 20,892 and Community/ Public Toilets constructed increased by 17,866 till date. Under solid waste management, 100% Door to door collection has increased to 86,403 wards and 100% Source Segregation has increased to 77,415 wards resulting in increase of the total waste processing to 70% as against 68% till 1st January 2021.
Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0: Hon’ble Prime Minister launched the second phase of Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 on 1st October, 2021 with an outlay of about ₹ 4.4 Lakh Crore to adopt ‘Universal Approach’ and make a move towards ‘Saturation’ in sanitation and water availability in all Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana –National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM)
The DAY-NULM is a flagship scheme which aims towards alleviating urban poverty through building strong community institutions, providing skill training, access to affordable credit for self-employment, support for street vendors and shelters for the urban homeless. Since inception, it has covered 28 states, 7 UTs and 3,806 Towns creating 25.60 livelihoods. Under the scheme, 1.30 lakhs shelter spaces were created for urban homeless and 66.70 lakhs women members were mobilised into 6.4 lakh Self Help Groups (SHGs).
Memorandum of Understandings (MoUs) were implemented with e-commerce giants like Amazon & Flipkart for selling over 2,000 products made by 5,000 SHG members on e-commerce portals across 25 States/ UT.‘SonChiraiya’ brand was launched with the aim to provide increased visibility and wider market access to the local ethnic products viz. handicrafts, food, apparel, decorative, etc.The Mission has provided 26.50 lakh Certificate of Vending (CoV) to urban street vendors to safeguard their rights. Mission has streamlined the process for payments of training fees to skill training providers through PAiSA Portal, which is centralized electronic platform for processing payments to the beneficiaries under the Mission.
AZADI KA AMRUT MAHOTSAV: As a part of the ongoing “AzadikaAmritMahotsav” of MoHUA, Revolving Fund (RF) support to Area Level Federation (ALF) i.e. federation of Self Help Groups through PAiSA Portal was operationalised on 30.09.2021.
PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi)
The PM SVANidhi was launched to empower street vendors, making them independent and self-sustainable. Under “SwadishtVyanjankiAadhunikDukaan (SVAD)”, MoHUA has signed MOU with Swiggy and Zomato providing a digital platform for Street Food Vendors (SFVs). Presently, over 8,486 SFVs have been onboarded and have generated sales of over ₹4.9 Crores.
Tie up with Digital Payment Aggregators (DPAs) like BharatPe, Mswipe, PhonePe, Paytm, Aceware were done to issue UPI ids, QR codes and digital training to the beneficiaries. Around 24.5 Lakh Street Vendors (SVs) have been onboarded digitally out of which 9.8 lakh vendors are Digitally active who have conducted 10.9 Crore Digital Transactions till date.
More than 42 Lakhs Eligible Loan Application under 1st Tranche and 773,986 Eligible Loan Application under 2nd Tranche were submitted. Out of these, more than 30 Lakhs loans under 1st Tranche and 46,931 loans under 2nd Tranche were sanctioned and more than 27 Lakhs loans under 1st Tranche and 33,471 loans under 2nd Tranche were disbursed. The loan total amount disbursed under 1st Tranche is ₹2656.97Crores and under 2nd Tranche is ₹66.62 Crores.
Urban Transport
One metro project i.e. Bangalore Metro Rail Project Phase 2A & 2B of length 58.19 kms at the completion cost of ₹14,788 Cr has been sanctioned in June, 2021. 31 kms of metro rail lines have been commissioned in the cities of Delhi, Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata and Nagpur.Under Make-in-India initiatives, the Ministry, in January, 2021, has issued a list of items where public procurement shall be done only from local suppliers. With driverless train operation on 94 km on Delhi Metro’s network, India is at 4th position in the elite league of world’s metro systems which operate drives less trains.
************




