India is effectively managing the delicate balance between increasing its coal mining output and strategically phasing down the polluting processes associated with coal mining. This approach aims to boost energy production while mitigating environmental impacts.
Chhattisgarh-based Coal India subsidiary Southeastern Coalfields Limited’s (SECL) Gevra and Kusmunda coal mines have secured the 2nd and 4th spot in the list of the worlds 10 largest coal mines released by WorldAtlas.com.
These two mines, each producing over 100 million tons of coal annually and accounting for around 10% of India’s total coal production, utilize some of the world’s largest and most advanced mining machines. Notably, they employ the “Surface Miner,” a cutting-edge technology that extracts and processes coal without blasting, promoting eco-friendly mining operations.

Coal Mining a Big Booster for Economic Growth
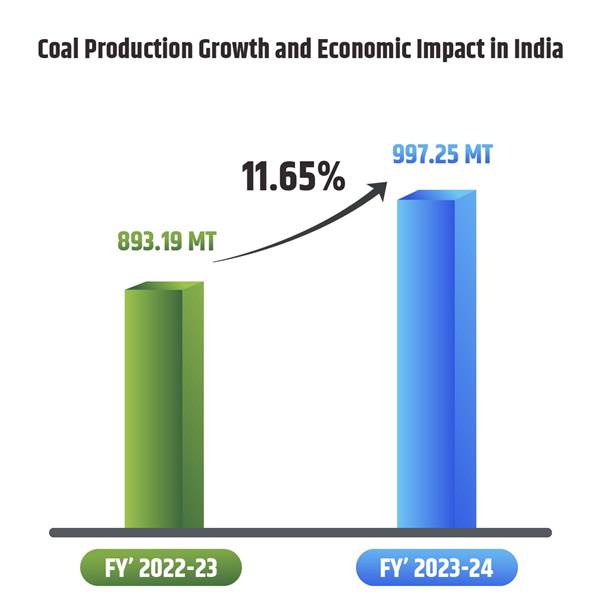
Through ongoing investment and a strong focus on modern technologies, India’s coal production reached 893.19 million tonnes in 2022-23. For 2023-24, production increased to 997.25 million tonnes, achieving an 11.65% growth. It is anticipated through comprehensive studies that coal demand in 2030 will likely reach 1462 MT and 1755 MT by 2047.
Coal mining sector has proved to be a big booster for economic growth of the coal producing States in the Country. State Governments are entitled to receive 14% of Royalty on sale price of coal. In case of captive/ commercial mines State Government are also entitled to receive the revenue share offered by the auction holder in transparent bidding process.
Apart from this, State Governments also benefit from increased employment, land compensation, increased investment in allied infrastructure like railways, roads and several other economic benefits.
The focus of the Central Government for enhancing coal production to meet the growing economy has directly helped the State Govts in realisation of additional revenue, which in turn has infused capital expenditure in the coal producing regions thereby bringing in development, both in infrastructure and social sector.
SUSTAINABILITY IN COAL MINES
The mining industry has long been associated with significant environmental degradation and resource depletion. However, in recent years, the concept of green mining has emerged as a beacon of hope for a sustainable future
Green Mining Led to a Sustainable Future
Green mining refers to the implementation of eco-friendly practices and technologies in the mining industry to reduce its environmental impact. It involves using renewable energy sources, recycling mine waste, minimizing water consumption, and employing sustainable extraction techniques.
The goal of adopting green mining is to mitigate the industry’s carbon footprint and promote responsible mining. To achieve environmental sustainability, the following is a brief explanation of the environmental protection measures being adopted by coal/lignite PSUs in coal mining areas
1. Air Quality Management
Effective air quality management in coal mines is essential for safeguarding the health of workers, protecting the environment, and ensuring sustainable mining operations. Coal mining activities often generate dust and emissions that can impact air quality both within the mine and in surrounding areas.
Implementing robust air quality management practices helps mitigate these impacts by controlling dust levels, monitoring emissions, and employing technologies to minimize pollution.
Wet drilling is used to reduce dust generation. Dust suppression systems are also included with drill machines. Surface miners and BWEs are being used more frequently, which reduces the need for drilling and blasting and, thus, the pollution load. Vehicles get routine maintenance in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications.

Fig. Mist Gun operation to control dust

Fig. PM 10 Analyser in CCL

Fig. Surface Miner with water jets, Gevra OCP, SECL

Fig. Mobile sprinklers in operation for suppression of dust
2. Mine Closure, Bio-reclamation & Land Use Management
Mine closure, bio-reclamation, and land use management are critical components of responsible coal mining practices aimed at minimizing environmental impacts and promoting sustainable land use. When a coal mine reaches the end of its operational life, a systematic approach to closure ensures that the site is safely and effectively rehabilitated.
Bio-reclamation involves restoring the ecological balance by reintroducing native flora and fauna, while land use management focuses on repurposing the land for beneficial uses, such as agriculture or recreational areas. Together, these practices help mitigate the environmental footprint of mining activities, support ecosystem recovery, and enhance the long-term usability of former mining sites.




Economic Significance of the Coal Sector Extends Beyond Energy Production
Single largest contributor to Railway Freight: Coal stands as the single largest contributor to railway freight, with an average share of nearly 49% of total freight income amounting to Rs. 82,275 Crore in the fiscal year 2022-23 alone. This revenue contribution has surpassed 33% of total railway earnings, showcasing the sector’s substantial influence on India’s transportation network.
Government Revenue: The coal sector contributes over Rs. 70,000 Crore annually to the central and state governments through royalties, GST, and other levies. These funds play a crucial role in fostering socio-economic development and infrastructure enhancement in coal-producing regions. Coal production generates substantial revenue for both Central and State Governments, with royalty collections reaching Rs. 23,184.86 Crore in the fiscal year 2022-23.
Employment: The coal sector provides enormous employment opportunities, particularly in coal-producing districts of Eastern States. With over 239,210 employees in Coal India Ltd and its subsidiaries, supplemented by contractual workers and outsourcing engagements, the sector sustains livelihoods for thousands of families. Additionally, over 65,000 contractual workers are engaged in mining operations with CIL and 37,000 workers are engaged through outsourcing for security, driver and housekeeping. With an average 24,000 trucks are engaged in coal transportation supporting 50,000 people and 30000, workers are engaged in captive/commercial coal mining companies contributing to job creation.
Dividend Payments: Coal India Ltd consistently contributes substantial dividends to the Central Government and has paid an average of Rs. 6,487 Crore annually over the past five years. The FY 2022-23 has seen a significant dividend payment of Rs. 9,475.85 Crore, highlighting the sector’s financial stability and contribution to government revenues.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Coal sector PSUs prioritize CSR initiatives, with an average annual expenditure of Rs. 608 Crore over the past five years. Notably, Coal India Ltd alone has allocated an average of Rs. 517 Crore annually for CSR activities. Over 90% of the expenditure has been incurred on, socio- economic development focusing on healthcare, education, water supply and skill development in coal-producing regions.
Capital Expenditure: Substantial investments in capital expenditure, averaging Rs. 18,255 Crore annually over the past five years, have facilitated infrastructure development and resource optimization within coal sector PSUs. This capital infusion stimulates economic growth and fosters a conducive environment for sustainable development.
As India continues its trajectory of growth and development, the coal sector remains a cornerstone of the nation’s progress, driving economic prosperity, employment generation, and social well-being.
Conclusion
India’s approach to balancing increased coal mining output with a strategic phase-down of pollution reflects a commitment to both economic growth and environmental stewardship. By enhancing coal production to meet rising energy demands while simultaneously implementing measures to reduce pollution, India is working towards a more sustainable and responsible mining industry. This dual focus on maximizing output and minimizing environmental impact demonstrates a forward-thinking strategy that aims to support economic development, improve air quality, and contribute to long-term sustainability in the coal sector.
References:
pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1941340
chap7AnnualReport2023en.pdf (coal.nic.in)
Sustainable Development for Coal Sector (pib.gov.in)
pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2009196
chap7AnnualReport2023en.pdf (coal.nic.in)
Press Information Bureau (pib.gov.in)
Click here to see in PDF
*****


















































You must be logged in to post a comment.