Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has issued advisory for COVID-19 testing during the second wave of the pandemic. It said, at present, the laboratories are facing challenges to meet the expected testing target due to extraordinary case load and staff getting infected with COVID-19. In view of this situation, it is imperative to optimize the RTPCR testing and simultaneously increase the access and availability of testing to all citizens of the country. In its advisory, the ICMR has recommended measures to optimize RTPCR testing. It said, RTPCR test must not be repeated in any individual who has tested positive once either by RAT or RTPCR. No testing is required for COVID-19 recovered individuals at the time of hospital discharge in accordance with the discharge policy of the Union Health Ministry.
Besides, the need for RTPCR test in healthy individuals undertaking inter-state domestic travel may be completely removed to reduce the load on laboratories. Non-essential travel and interstate travel of symptomatic individuals should be essentially avoided to reduce the risk of infection. All asymptomatic individuals undertaking essential travel must follow COVID appropriate behaviour. The ICMR said, mobile testing laboratories are now available on GeM portal and States are encouraged to augment RTPCR testing through mobile systems.
With regard to measures to ramp up testing through Rapid antigen test (RAT), the ICMR said, RAT may be allowed at all available Government and private healthcare facilities. Dedicated RAT booths should be set up in cities, towns and villages to offer testing to people. It said, testing booths may be set up at multiple locations including healthcare facilities, RWA, offices, schools, colleges, community centers and other available vacant spaces. These booths should be operational round the clock to improve access and availability of testing. It has also suggested that stringent measures must be instituted to avoid overcrowding at RAT testing facilities.
The ICMR said, all states are advised to ensure full utilization of the available RTPCR testing capacity, both in public and private laboratories.
Symptomatic individuals identified positive by RAT should not be re-tested and advised to go through home-based care as per ICMR guidelines. It said, symptomatic individuals identified negative by RAT should be linked with RTPCR test facility and in the meantime be urged to follow home isolation and treatment. It said, all RTPCR and RAT test results should be uploaded on ICMR portal. It also said that the vaccination status of all individuals tested for COVID-19 must be entered into the Sample Referral Form (SRF) in the RTPCR app both for individuals tested by RTPCR and RAT as this information is of critical importance.
Month: May 2021
Govt identifies 581 sites for setting up medical oxygen plants in various states
Government has identified 581 sites for setting up additional Pressure Swing Absorption (PSA) medical oxygen plants in various states. In a series of tweets, Road, Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said, National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) will be the nodal agency for executing civil and electrical work for these plants and will complete them on war footing.
He said, our engineers will work with the doctors to ensure oxygen supply to needy patients. The Minister said, like record speed in roads, NHAI will construct infrastructure in record speed to save life of every Indian.
India, UK adopt Roadmap 2030 to elevate bilateral ties to comprehensive Strategic Partnership
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his British counterpart Boris Johnson have adopted an ambitious ‘Roadmap 2030’ to elevate bilateral ties to a ‘Comprehensive Strategic Partnership’. The Roadmap will pave the way for a deeper and stronger engagement over the next ten years in the areas of people to people contacts, trade and economy, defence and security, climate action and health.
In a Virtual Summit held yesterday, the two leaders discussed the Covid19 situation and ongoing cooperation in the fight against the pandemic, including the successful partnership on vaccines. Prime Minister Modi thanked Prime Minister Johnson for the prompt medical assistance provided by the UK in the wake of the severe second wave of Covid19 in India. Prime Minister Johnson appreciated India’s role in extending assistance to the UK and other countries over the last year, including by way of supply of pharmaceuticals and vaccines.
The two Prime Ministers launched an ‘Enhanced Trade Partnership’ to unleash the trade potential by setting an ambitious target of more than doubling bilateral trade by 2030. As part of the ETP, India and the UK agreed on a roadmap to negotiate a comprehensive and balanced FTA, including consideration of an Interim Trade Agreement for delivering early gains. The enhanced trade partnership will generate several thousands of direct and indirect jobs in both the countries.
A new India-UK ‘Global Innovation Partnership’ was announced at the Virtual Summit that aims to support the transfer of inclusive Indian innovations to select developing countries, starting with Africa. Both sides agreed to enhance cooperation on new and emerging technologies, including Digital and ICT products, and work on supply chain resilience. They also agreed to strengthen defence and security ties, including in the maritime, counter-terrorism and cyberspace domains.
Both Prime Ministers also exchanged views on regional and global issues of mutual interest, including cooperation in the Indo-Pacific, and G7. They reiterated commitment to climate action to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement and agreed to closely engage in the run up to CoP26 hosted by the UK later this year.
India and the UK also launched a comprehensive partnership on migration and mobility that will facilitate greater opportunities for the mobility of students and professionals between the two countries.
Call for Papers IJR
Why to publish a paper with IJR?
- The papers of this journal has an open access to all
- Great source of reviewers from academics as well as industries.
- Rapid publication.
- Authors will get INDIVIDUAL SOFT COPY THE CERTIFICATE.
- High Impact Factor
- Indexed in more than 20 reputed databases
- Nominal fees of publication / Article Processing Charges
- 8 Years of track record
- 2300+ papers indexed in google scholar
- Served 7000+ authors from more than 40 countries
- A team of 200+ Editors and Reviewers from reputed institutes over the world
How to publish a paper?
Many primary authors may deal with this question, many of us may have innovative ideas to be published but they may not know the general steps of publishing a paper. The publication of the paper is simply done as per the following steps.
- Research over the topic
- Study what others have done
- Finalize your key area of research
- Work over the idea
- Prepare a draft(generally 6-8 pages)
- Revise the draft
- Check for the grammatical mistakes
- Check for the plagiarism
- Revise the draft
- Get opinion of other on your draft
- Make final corrections
- Submit the paper to the journal
- Wait for the reviewers comments
- Correct the paper and resubmit
- Complete the registration
- Congratulations!!! Your paper is published
Easy way of paper publication
IJR is trying to make the paper publication easy for the authors. We are working on reduction of the time for completion of the review process for the paper. The paper publication for the authors is a great learning experience where one can understand how to analyze, create, prepare, present and revise the technical details.
Invitation for journal publication
IJR invites the manuscripts in the areas of Engineering, Technology, and Sciences. All the areas of these broad categories are cover under the scope of IJR. The authors are requested to submit the original creativity of the data to this journal publication.
Formal Conditions of Acceptance:
- English is the compulsory language for the paper
- Paper should be original and should avoid the plagiarism
- Paper should present some contribution to the scientific research
How to Submit Papers
Garden City
The garden city movement is a method of urban planning in which self-contained communities are surrounded by “greenbelts”, containing proportionate areas of residences, industry and agriculture. The idea was initiated in 1898 by Sir Ebenezer Howard in the United Kingdom and aims to capture the primary benefits of a countryside environment and a city environment while avoiding the disadvantages presented by both.
Inspired by the utopian novel “Looking Backward” and Henry George’s work “Progress and Poverty”, Howard published the book “To-morrow: a Peaceful Path to Real Reform” in 1898 (which was reissued in 1902 as “Garden Cities of To-morrow”). His idealized garden city would house 32,000 people on a site of 6,000 acres, planned on a concentric pattern with open spaces, public parks and six radial boulevards, 120 ft (37 m) wide, extending from the centre. The garden city would be self-sufficient and when it reached full population, another garden city would be developed nearby. Howard envisaged a cluster of several garden cities as satellites of a central city of 58,000 people, linked by road and rail.
Howard believed that all people agreed the overcrowding and deterioration of cities was one of the troubling issues of their time. It is important to understand the context to which Howard’s work was a reaction. London (and other cities) in the 19th century were in the throws of industrialization, and the cities were exerting massive forces on the labour markets of the time.
Massive immigration from the countryside to the cities was taking place with London. This situation was unsustainable and political commentators of all parties sought “how best to provide the proper antidote against the greatest danger of modern existence”. To Howard the cure was simple – to reintegrate people with the countryside.
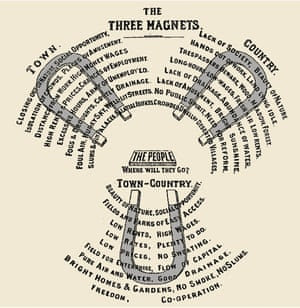
Concept of Three magnets
He had no training in urban planning or design but excelled in creating places which he called “magnets” where people would want to come to reside and work. His garden cities were planned, contained communities surrounded by a green belt (parks), containing proportionate areas of residences, industry and agriculture. Garden city movement aimed at addressing the urban problems plaguing the industrial city of that time. Garden city concept was an effective response for a better quality of life in overcrowded and dirty industrial towns which had deteriorated the environment and posed serious threat to health.
Garden city movement had the “Three Magnets” to addresses the question ‘Where will the people go?’ the choices being ‘Town’, ‘Country’ or ‘Town Country’.
Town
- Social opportunity
- Closing out of nature
- Isolation of crowds
- High rents and prices
- Places of amusement
- Foul air and murky sky
- Chances of employment
- Slums and gin palaces
- High money wages
- Costly drainage
- Well-lit streets
- Palatial edifices
Country
- Beauty of nature
- Lack of society
- Land lying idle
- Hands out of work
- Wood, meadow, forest
- Trespassers beware
- Fresh air
- Low wages
- Low rents
- Lack of drainage
- Abundance of water
- Lack of amusement
- Bright sunshine
- No public spirit
- Need for reform
- Crowded dwellings
- Deserted villages
Town- Country
It was a combination of both town and countryside with aim of providing benefits of both and offered beauty of nature, social opportunity, fields if easy access, low rent, high wages and field of enterprise. Thus the solution was found in a combination of the advantages of Town and Country – the ‘Town Country Magnet’ – it was proposed a town in the country, and having within it the amenities of natural beauty, fresh air and healthfulness. Thus advantages of the Town – Country are seed to be free from the disadvantages of either. Town-country combination has the advantages of both aspects.
- Beauty of nature
- Peace all-over the places
- Social opportunity
- Cumulative growth
- Fields and parks of easy access
- Equal chances
- Low rents- high wages
- Low rates- plenty to do
- Low prices- no sweating
- Field for enterprise- flow of capital
- Pure air and water- good drainage
- Bright homes & gardens- no smoke, no slums
- Freedom- co-operation
Principles of Garden City
- Co-operative holding of land to insure that the advantage of appreciation of land values goes to the community, not the private individuals
- Economic and social advantages of large scale planning
- Establishment of cities of limited size, but at the same time possessing a balanced agricultural industrial economy
- Urban decentralization
- Use of a surrounding green belt to serve as an agricultural recreational area
Features of Garden City
Circular city growing in a radial manner or pattern
- Divided into six equal wards, by six main Boulevards that radiated from the central park/garden
- Civic institutions (Town Hall, Library, Hospital, Theatre, Museum etc. ) are placed around the central garden
- The central park enclosed by a crystal palace acts as an arcade for indoor shops and winter gardens
- The streets for houses are formed by a series of concentric ringed tree lined avenues
- Distance between each ring vary between 3-5km
- A 420 feet wide, 3 mile long, Grand avenue which run in the center of concentric rings , houses the schools and churches and acts as a continuous public park
- The municipal railway was placed in another ring closer to the industrial ring, so that the pressure of excess transport on the city streets is reduced and the city is connected to the rest of the nation.
Main components of Howard’s Garden city movement
1) Planned Dispersal
2) Limit of Town Size
3) Amenities
4) Town and Country Relationship
5) Planning Control
6) Neighborhoods
Letchworth Garden City
- Its plan was based on population of 30000 with living area of 1250 acres and 2500 acres of rural green belt.
- Communities ranged from 12000 – 18000 people, small enough which required no vehicular transportation.
- Industries were connected to central city by rapid transportation.
- In 30 years, the city developed with 15000 population and 150 shops, industries.
Welwyn Garden City
- It started with area of 2400 acres and 40000 populations.
- Had a parkway, almost a mile long central mall.
- Town laid out along tree-lined boulevards with Neo Georgian town center.
- Every road had a wide grass verge.
- In 15 years – developed with 10000 population and 50 shops, industries.
Failure of Garden Cities
Over 1 crore 66 lakh people recovered from COVID-19 infection in country so far
The number of total active cases of COVID-19 in the country further swelled up today to comprise nearly 17 percent of the total reported cases. The Health Ministry has informed that currently over 34 lakh 47 thousand people are reported to be suffering from the viral pandemic and are either hospitalised or are under home isolation.
In the last 24 hours, the nation registered 3 lakh 57 thousand 229 new COVID cases. With this the recovery rate has further slipped to stand at 81.91 per cent.
Since yesterday over 3 lakh 20 thousand people have been discharged from Hospitals or are reported to have been completely cured. So far, over 1 crore 66 lakh people have recovered from the COVID-19 infection in the country. Ten States including Maharashtra, Karnataka, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat & Kerala continue to be the major hotspots of the viral pandemic. Nearly 75 per cent of the new cases are reported from these 10 states. The Health Ministry has informed that three thousand 449 COVID related deaths were reported in the last 24 hours taking the cumulative toll to 2 lakh 22 thousand 408.
With a special focus on the 5-point principle of ‘Test, Track, Treat, Isolate & Vaccinate’, the number of cumulative COVID-19 testing reported by Indian Council of Medical Research, ICMR has surpassed the figure of 29 crore 33 lakh. The apex medical research body has informed that in the past 24 hours more than 16 lakh 63 thousand samples were tested in the country. As of today, two thousand 506 laboratories are engaged in the work of testing COVID samples across the country which includes one thousand 241 government and one thousand 265 private labs.
Education Ministry asks all centrally funded institutions to postpone offline examinations scheduled in May
Union Education Ministry has written to all centrally funded institutions to postpone their offline examinations scheduled in the month of May this year in view of COVID surge. In a letter addressed to all the heads of centrally funded institutions, Secretary, Higher Education Amit Khare has urged the Institutions to postpone all offline examinations scheduled in the month of May. The Online examinations may however continue as scheduled.
The letter also stated that the decision will be reviewed in the first week of June. All Institutions have been asked to encourage everyone eligible to get vaccinated and also ensure all possible help in every regard.
Centre waives off IGST on import of Corona related medical supplies
In a major relief, Centre has waived off IGST on the import of COVID related medical supplies including Remdesivir Injection/API, Medical Oxygen, O2 Concentrators, Cryogenic tanks & COVID Vaccines among others. The exemption has been granted till 30th June for free distribution of these medical supplies.
Earlier the Centre had waived the import duty & health cess on such medical supplies.
This exemption will enable import of the COVID relief supply imported free of cost for free distribution without payment of IGST. State Governments have been asked to appoint a nodal authority to facilitate the importers to avail the relief exemption.
PM Modi reviews growing need of human resources required to deal with Covid-19 crisis
Prime Minister Narendra Modi reviewed the growing need of human resources required for dealing with the crisis of Covid-19 situation in the country.
Many important decisions have been taken during the review meeting which will significantly boost availability of medical personnel required for treatment of Covid patients.
Among the many decisions, a decision has been taken to postpone NEET-Post Graduate exam for at least four months.
This will ensure the availability of qualified doctors for Covid duties.
The exam will not be held before 31st of August of this year and students will be given at least one month of time after the announcement of the exam.
It has also been decided to allow deployment of medical interns in the Covid management duties under the supervision of their faculty.
The services of final year MBBS students can be utilized for providing services like tele-consultation and monitoring of mild COVID cases.
The services of final year post graduate students as residents may continue to be utilized.
It has further been decided that services of B.Sc. and General Nursing and Midwifery nurses may be utilized in Covid nursing duties under the supervision of Senior Doctors and Nurses.
In a major decision, it has been decided that the individuals providing services in COVID management will be given priority in forthcoming regular government recruitments after they complete a minimum of 100 days of COVID duties.
The medical students and professionals sought to be engaged in COVID related work will be suitably vaccinated.
Engaged Health professionals will be covered under the Insurance Scheme of Government.
All such professionals will be given the Prime Minister’s Distinguished COVID National Service Samman after completion of their 100 days of COVID duties.
The States and Union Territories have been requested to consider the above incentives to maximise the availability of manpower to provide relief to the Covid patients.
More than 84,000 beneficiaries from 18 to 44 age group receive first dose of Corona vaccine on first day of 3rd phase inoculation
Government has said 84 thousand 599 beneficiaries of the age group 18 to 44 years received their first dose of COVID vaccine yesterday. The Liberalised and Accelerated Phase-3 Strategy of Covid-19 Vaccination came into force yesterday. The registration for the newly eligible population groups has commenced on 28th of last month.
Union Health Ministry said, the total vaccination across the country has crossed more than 15 crore 66 lakh mark. These include over 94 lakh 28 thousand Healthcare Workers who have taken the 1st dose and more than 62 lakh Health care workers who have taken the 2nd dose. Over one crore 26 lakh Frontline Workers have taken the 1st dose and more than 68 lakh front line workers have taken the 2nd dose.
The Ministry said, the country has administered more than 16 lakh vaccine doses till 8 pm yesterday. Out of which around ten lakh beneficiaries were vaccinated for 1st dose and six lakh 58 thousand beneficiaries received 2nd dose of the vaccine.
The Central Government has advised the States and Union Territories to set up Help Desks with the aid of Volunteer Groups, NGOs, and Civil Society Organisations. The Help Desk Team set up at the hospitals can support in managing the patients being admitted in the hospital effectively and facilitate better interaction between hospital staff and patients’ attendants.
They may also help in increasing awareness about the necessary safety precautions and appropriate COVID-19 behavior amongst patients. Similarly, NGOs can also help in other activities at hospitals that facilitate the attendants’ grievance redressal and in logistic requirements such as helping with discharging, liasoning with cremation grounds and burial grounds.
The Central Government along with States and UTs through a ‘Whole of Government’ approach has embarked on a five-point strategy for prevention, containment, and management of the COVID-19 pandemic in the country. Vaccination forms an integral component of the five-point strategy including Test, Track, Treat, and COVID Appropriate Behaviour.
Oxygen Express to deliver record 250 tonnes of liquid medical oxygen to Delhi, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh today
Railway Ministry has said that Oxygen Expresss will deliver a record 250 tonnes of liquid medical oxygen to Delhi, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh by today. Accelerating its pace of delivering liquid medical oxygen to various states, Indian Railways has delivered more than 813 tonnes of Liquid Medical Oxygen in 56 tankers to various states across the country.
According to Railway, 174 tonnes of liquid medical oxygen have been delivered to Maharashtra, more than 356 tonnes to Uttar Pradesh, over 134 tonnes to Madhya Pradesh, more than 79 tonnes to Haryana and 70 tonnes to Delhi. The Ministry said, 14 Oxygen expresses have already completed their journey and five more loaded Oxygen express are on the run carrying 342 tonnes of oxygen.
Delhi is set to receive its 2nd Oxygen Express with 120 tonnes of Liquid Oxygen by this evening. Telangana will also receive its first Oxygen express currently on the way from Angul carrying over 124 tonnes of liquid medical oxygen. The Ministry said, Haryana received its first and second Oxygen express yesterday carrying 79 tonnes of oxygen in five tankers.
Counting of votes begins for assembly elections in Assam, West Bengal, Kerala, Tamil Nadu & Puducherry
Counting of votes has begun for assembly elections in Assam, West Bengal, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Puducherry. Counting began at 8 this morning. Assembly elections in these states and union territory were held from March 27 to April 29. Counting of votes for bypolls to four Lok Sabha and 12 Assembly seats in different states is also underway.
Trends and results will be available on the Election Commission website and will be updated every few minutes to display the current round wise trends and results of each constituency. The trends and results will also be accessible through the “Voter helpline” Mobile App.
In view of second wave of pandemic and with a view to ensure a completely COVID safe arrangements during counting, the Election Commission has rolled out strict COVID protocols for the counting day. The District Election Officer has been appointed as the Nodal Officer at each Counting Centre to ensure adherence to the COVID-19 related norms at the centre. Local Health Authorities have also been mandated to issue compliance certificate in respect of the Counting Centres.
As per the safety measures, no candidates or poll agents is being allowed inside the counting hall without undergoing RT-PCR or Rapid Antigen Test. However, those who have been administered both the doses of COVID vaccination have been allowed. The Commission has also prohibited public gathering outside the counting venue during the process of counting.
At the entry of hall, room and premises, Thermal Scanning of all persons are being carried out and sanitizer, soap and water have been made available.
No one having any symptom of COVID-19 like fever, cold are allowed to enter in the Counting Hall. Candidate will be allowed to appoint/replace the Counting Agents in case report is positive. Social distancing will be maintained inside Counting Hall. Seating arrangement of counting personnel and agents etc will be made as per COVID-19 guidelines of NDMA and SDMA. There will be sufficient number of PPE Kit for Counting Agents and Candidates. Masks, Sanitizer, Face-Shields and Gloves are being provided to every counting official and security personnel.
The Election Commission has already banned all victory processions on or after the day of counting. Not more than two people will be allowed to accompany the winning candidates to receive the certificate of election from the concerned Returning Officer.
In Kerala, the counting of votes in 140 constituencies has begun. AIR correspondent reports that postal votes courting began at 8 in the morning today and the votes in EVM’s will be counted from 8.30 am onwards. Counting is taking place in 633 halls in 114 centers across the state. In the present alarming covid scenario in the State all arrangements are done for the strict abidance to covid protocol.
All officials, media and political agents with negative RTPCR test are only allowed in the counting premises. As more number of postal votes are there this time, the final result is expected to slightly delay from last time. As just few hours are left to know who will rule Kerala for the next 5 years, all the three major front , LDF, UDF and NDA are equally exuding confidence that the mandate will be in their favour.
In Tamil Nadu, counting of votes began at eight this morning for all the 234 Assembly constituencies and the lone Loksabha seat of Kanyakumari. AIR correspondent reports that the fate of 3998 candidates sealed on the 6th of April will be decided today. Tamil Nadu despite covid situation had registered 72.81 percentage of votes. Postal ballots have been taken up for counting in the first round in all the districts. Till yesterday over five lakh 64 thousand postal votes have been registered.
A total of 16 thousand 387 people are involved in counting in 75 counting centres in the State. Security has been stepped up with one lakh police personnel on duty today. Election Comission has banned victory marches due to the pandemic situation, Political party leaders have also appealed to their party members to remain indoors and celebrate.
As election commission had allowed only covid negative persons on counting duty last minute changes had to be made by parties and officials as more than 400 persons had tested positive. CCTV cameras have been installed in all the counting centres. In each counting centre votes from four to five constituencies will be counted. 14 tables will be set up for counting votes for each constituency.
In Puducherry, counting of postal ballots is underway. AIR correspondent reports that the counting of votes, of 23 constituencies in Puducherry region is held in 3 centres here. In order to reduce the number of counting agents, the Election department has planned to count the votes in 3 batches of constituencies. i.e 8, 8 and 7 constituencies at around 10 am, 1 pm and 6 pm respectively.
Only the agents of 8 constituencies are allowed to assemble in the centre at a time. To maintain social distancing in the counting hall, the number of tables for counting in each hall is restricted to 5. Arrangements have been made strictly according to the Covid protocols. Face masks, sanitizers hand gloves and PPE KITs provided to the staffs.
All the 3 centres were sanitized yesterday. Around 1000 officials involved in the counting process and 400 policemen along with Central forces deployed here for security purpose. Apart from that a Health Officer is also available in each centre with an Ambulance for emergency medical care. The votes of 5 Constituencies in Karaikal, and each one in Mahe and Yanam are counted in the respective regions.