
Anatomy is the study of the shape and structure of the body of organisms or living beings. The word anatomy is derived from the Greek words ‘ ana ‘ and ‘ tomy ‘ where ‘ ana ‘ means ‘apart’ and ‘tomy ‘ means ‘to cut’. In physiology, the functions of various system such as respiratory system, digestive system, nervous system, skeleton system and muscular system of organisms are studied. It can be said that physiology is the study of how the body and all its part function. It consists of two word, namely, ‘physio’ and ‘ ology’ where ‘physio’ means ‘nature ‘ and ‘ ology ‘ means ‘ study’. Here ,we will study human anatomy and human physiology.
Definition of Human Anatomy
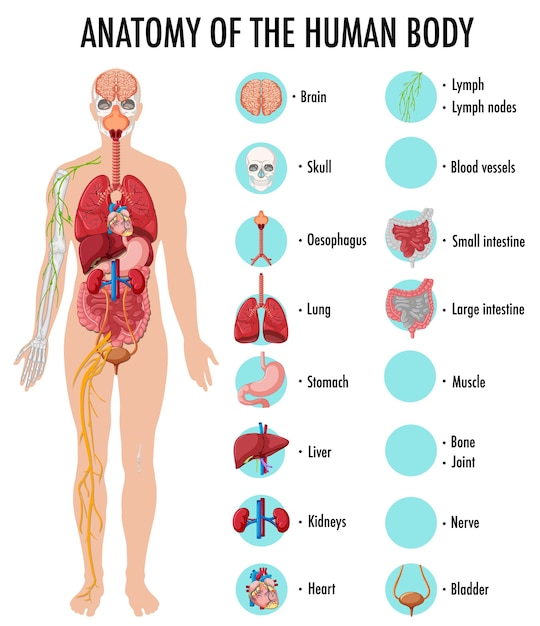
Human Anatomy is the study of structure ,shape, size , weight and location of all the organs of human body. A detailed knowledge of the structure of various system of human body is provided in human anatomy . For example , the shape, size, weight, structure and location of all the organs of the excretory system such as lungs, kidneys, large intestine, liver, skin, etc. are studied in human anatomy. Human anatomy can be defined as the science dealing with human body structure and relationships among structures.
Importance of Anatomy
The importance of anatomy and physiology is mentioned below.
- Anatomy Provides the Knowledge of Structures of Various Organs : Human anatomy provides the detailed knowledge of the structure of various organ body . We get the knowledge of structure, shape, size, location and weight of organs of all the systems of our body. We come to know about the length of various organs such as the length, size and shape of the bones. With the help of anatomy , we get the knowledge of the percentage of white fibres and red fibres present in an individual. As a result of such knowledge , the teacher and coaches working in the field of physical education and sports may easily select the suitable sports according to the traits of students. For example, weightlifting is more appropriate for short statured students, who have more percentage of white fibres i.e., fast twitch fibres in comparison to red fibers i.e., slow twitch fibres can perform better in sprinting events instead of endurance events.



You must be logged in to post a comment.