To enhance the quality of education across the country, the Government of India has taken following steps:
- Samagra Shiksha: Samagra Shiksha an integrated scheme covering all classes from pre-primary to senior secondary has been revamped and aligned with the recommendations of NEP 2020. The scheme aims to ensure that all children have access to quality education with an equitable and inclusive classroom environment which should take care of their diverse background, multilingual needs, different academic abilities and make them active participants in the learning process. The scheme has been extended for a period of five years i.e., from 2021-22 to 2025-26. Samagra Shiksha is providing support for many interventions including implementation of major NEP recommendations such as emphasis on Foundational Literacy and Numeracy, provision for Holistic Progress Card (HPC), Capacity building of teachers (50 Hrs CPD), Bagless days and internships, support for OOSC in age group of 16- 19 years, Separate stipend for CWSN girl child, identification of CWSN and Resource Centre at block level, expansion of schooling facilities including Residential Hostels, KGBVs, and vocational education etc.
- SARTHAQ: In pursuance of the goals and objectives of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 issued on 29th July, 2020 and to assist States and UTs in this task, the Department of School Education and Literacy has developed an indicative and suggestive Implementation Plan for School Education, called ‘Students’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement through Quality Education (SARTHAQ)’.This implementation plan was released on 8th April 2021. The plan keeps in mind the concurrent nature of education and adheres to the spirit of federalism. States and UTs are given the flexibility to adapt this plan with local contextualization and also modify as per their needs and requirements. This implementation plan delineates the roadmap and way forward for implementation of NEP, 2020 for the next 10 years, which is very important for its smooth and effective implementation.
- National Achievement Survey (NAS) 2021 : NAS was conducted for grade- 3, 5, 8 & 10 on 12th Nov 2021 by the Ministry of Education to evaluate children’s progress and learning competencies as an indicator of the health of the education system, to take appropriate steps for remedial actions at different levels. About 1,18,000school participated in NAS 2021 About 34 lakh students from 718 Districts, including 22 lakh from rural areas and 11 lakh from urban areas, have appeared in NAS 2021
- NISHTHA : An integrated teacher training programme 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0 has been introduced for different stages of school education – Teachers, Head Teachers/Principals and other stakeholders in Educational Management and Administration –
- NISHTHA 1.0 for Elementary level (Classes I-VIII). The course has been completed by nearly 41 lakh stakeholders.
- NISHTHA 2.0 for Secondary level (Classes IX-XII) targeted for 10 lakh teachers.
- NISHTHA 3.0 for NIPUN Bharat (ECCE to Class V) targeted for 25 lakh teachers.
NISHTHA, for “Improving Quality of School Education through Integrated Teacher Training” has been conducted in the states/UTs with the aim to build competencies among all the teachers and school principals.
NISHTHA (National Initiatives for School Heads and Teacher’s Holistic Development) was launched online through DIKSHA. 33 States/ UTs and 8 autonomous organizations under MoE, MoD and MoTA initiated NISHTHA 2.0 (Secondary) in 10 languages – Hindi, English, Urdu, Gujarati, Punjabi, Telugu, Kannada, Bengali, Marathi and Odia. Under NISHTHA 3.0 (FLN) 28 States/UTs and five autonomous organizations under MoE (KVS, CBSE, CISCE, AEES, and CTSA) initiated NISHTHA 3.0 (FLN) in 8 languages – Hindi, English, Urdu, Gujarati, Telugu, Kannada, Odia and Mizo.
- Learning Outcomes : Learning Outcomes for Secondary level was notified on 23.12.2019. LOs for senior secondary level have been developed and draft document has been shared with States and UTs for feedback.
- NIPUN Bharat : National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy (NIPUN Bharat) has been launched under Samagra Shiksha on 5th July 2021, for ensuring that every child in the country necessarily attains foundational literacy and numeracy (FLN) by the end of Grade 3. The goals and objectives of the mission are required to be achieved by all Govt., Govt. Aided and Private Schools so that universal acquisition of FLN skills can be achieved.
- VIDYA PRAVESH (A School Preparation Module) : NEP-2020 has recommended the development of ‘3-month play-based ‘school preparation module’ for all Grade 1 Students’ with and without preschool education by the NCERT’, as an interim measure to ensure that all children are grade I ready till universal provisioning of quality preschool education is achieved. Accordingly, the NCERT has developed a 3 Months Play Based ‘School Preparation Module’ Vidya Pravesh launched on 29th July 2021 that can be adapted or adopted by States and UTs as per their need.
- NEP Achievements Booklet: The National Education Policy 2020(NEP:2020) envisions a substantial transformation in the entire education system at all stages right from Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) to higher education. It envisages education as a continuum without any segmentation and focuses on making education more experiential, holistic, integrated, character-building, inquiry-driven, discovery-oriented, learner-centred, discussion-based, flexible, and above all, more joyful. In this context, the implementation of NEP 2020 has been taken in a mission mode and 62 major milestones have been accomplished which will transform the school education sector.
- FLN tools and Resources at DIKSHA: DIKSHA (Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing) is the national digital platform for school education in India, aims to enable access to digital learning for students and teachers irrespective of their socio-economic backgrounds. It is in the form of a free mobile application and web portal available for use anywhere, anytime and for anyone. Under DIKSHA, a separate vertical for FLN resources has been developed to assist and mentor States/UTs and teachers for implementing NIPUN Bharat guidelines.
- Home learning guidelines : The role of parents and caregivers besides school, teachers, community, and volunteers is pivotal in supporting Home-based learning for their children, especially during this period of Covid-19. In view of this, Guidelines for Parent Participation in Home-based Learning during school closure and beyond have been developed. Guidelines shared with States/UTs vide letter dated 18.6.2021 to disseminate to all stakeholders on a wide scale and along with to translate the document into regional languages and use local context for easy access, understanding and widespread use.
- ICT and smart class approvals : Under the Information & Communication Technology (ICT) component of the Smagra Shiksha Scheme, there is a provision to impart computer literacy and computer-enabled learning to children, by developing and deploying curriculum-based interactive multimedia, digital books, virtual labs etc. across the country. It supports the establishment of smart classrooms, and ICT labs in schools, including support for hardware, educational software and e-content for teaching. It envisages covering all Government/Government-aided schools with classes VI to XII.
Till 2021-22, ICT Labs have been approved in 1,14,917 schools and Smart classrooms in 58,499 schools across the country.
- Exemplar school: The Finance Minister in her Budget speech on 01.02.2021 has announced to qualitatively strengthen more than 15,000 schools from across the country to include all components of the National Education Policy, 2020.
The objective is to develop them as exemplar schools in their regions, handholding and mentoring other schools to achieve the ideals of the National Education Policy. A draft proposal has been prepared for implementation of the Scheme for approval of Competent Authority.
- Bridge course and AAC by NCERT : NCERT has developed a bridge course for Out of School Children (OoSC) studying in special training centres age group from 6 to 14 years under the provision of Right to Education Act, 2009. The course aims to bridge the learning gaps and help children to be main streamed in regular school. The bridge course also comes with a teacher handbook, which helps the teacher in transaction and assessment of the competencies to bridge the learning gap.
- Alternative Academic Calendar (ACC) : An Alternative Academic Calendar (ACC) for all the stages of school education resources along with textbooks has been developed for school students. Following this calendar, students of all classes can receive school education systematically at home with the help of their teachers through available technological and social media tools till their school gets open. Parents of primary and upper primary students will be guided by teachers about the activities to be conducted with children using mobile phone, SMS, radio, television or various other social media. These activities are related to their syllabus and learning outcomes. Teachers will also be able to guide students by establishing contact with them through mobile phones or social media.
- Guidelines for main streaming of Children of Migrant Labourers : Department has issued guidelines for main streaming of Children of Migrant Labourers on 13th July 2020, allowing for their smooth admissions into schools without asking for any documents other than identity.
- Guidelines for main streaming of out-of-school children : To ensure that children have access to education with quality and equity and to minimize the impact of the pandemic on school education in the country, the Department of School Education has prepared and issued detailed guidelines on 7th January, 2021, on the steps to be taken by the States and UTs. The guidelines, among others, include identification of out of school children from age 6-18 years, enrolment drives and awareness generation, student support while schools are closed, continued Education for children with Special Needs (CWSN), student support on school reopening and Teacher capacity building.
- Comprehensive COVID Action plan : The Department of School Education and Literacy vide letter dated 4th May, 2021 has shared the Covid Action plan with States/UTs and other stakeholders for mitigating the loss of learning. Various focus areas and interventions for implementing this roadmap include:
- Preventing drop outs, locating Out of School Children and mainstreaming them.
- Tracking children and their learning levels.
- Mitigating learning loss – Developing effective home-learning programmes and tracking learning.
- Helping teachers reach the last child in the last mile using multiple modes – portal, apps, telecast/broadcast, online/offline etc.
- Teacher capacity building.
- Support to schools.
- Systematic involvement of parents, community, local self-governments, volunteers, etc.
- Health and safety of teachers and students should be of paramount importance while designing any intervention.
- SAFAL: Structured Assessment for Analyzing Learning levels (SAFAL) has been developed by CBSE and launched on 29th July 2021. Competency-based assessment will be introduced in CBSE schools for grades 3, 5 and 8 as per NEP 2020, this assessment will focus on testing for core concepts, application-based questions and higher order thinking skills. SAFAL will ensure progress throughout school years by providing diagnostic information about students’ learning to schools and thus, support school education to move towards competency-based education. The pilot for key stage assessment of classes 3, 5 & 8 will be undertaken in February 2022.
- TERMs : Central Board of Secondary Education has developed Teacher Energized Resource Material (TERM) handbooks that will aid teachers in aligning their classroom transactions to a competency framework. To begin with these, handbooks have been developed for two subjects – science and mathematics covering the entire syllabus of grades 6 to 10. Each chapter of the resource material corresponds to the respective chapters in the NCERT textbooks.
- Handbook on 21st-century skills : A handbook on 21st Century Skills has been prepared by the Central Board of Secondary Education to provide a clear understanding of 21st-century skills and also to collectively collaborate towards attaining these skills in each learner.
21.Student learning enhancement guidelines : Learning Enhancement Guidelines have been prepared by NCERT which suggest models for the following three types of scenarios to ensure that no child is deprived of reach of education:
a) Learning Enhancement during COVID-19 for students without digital devices;
b) Learning Enhancement during COVID-19 for students with limited access to digital devices &
c) Learning Enhancement during COVID-19 for students with digital devices.
i. Learning Enhancement Programme and Remedial Teaching : Under Samagra Shiksha, remedial teaching and bridge courses have been used at the elementary level and Learning Enhancement Programme (LEP) has been implemented to address the challenges at the secondary level. The students are provided with suitable assistance and guidance following their abilities and learning needs so that they can develop their potential to the maximum extent. The objective of LEP is to identify the learning gaps and equip students with the core learning pre-requisites appropriate for the particular grade. LEP also includes various activities under PBBB for early grades.
ii. Teacher resources on MOOCs on experiential learning and competency-based learning : MOOC stands for Massive Open Online Course, offer unlimited participation (massive) and are open access, freely available via various sites. There are Special activity-based and highly engaging modules prepared on the pedagogies related to experiential learning and competency-based learning to mitigate the impact of the pandemic. MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) pertaining to school and higher education are being offered through SWAYAM Portal. NCERT offers 30 courses for Classes XI and XII covering 11 subjects through SWAYAM portal.
iii. Comic books : Department of School Education & Literacy, in its endeavour to provide holistic learning to students has launched comic books aligned to chapters of NCERT textbooks. 100+ comic books have been launched created by teachers of CBSE affiliated schools and curated by NCERT on 24th March 2021. This innovative initiative will help in increasing the cultural and social sensitivity in our children while imparting knowledge and in continuing their learning through joyful means and also acquire/augment 21st-century skills even during the pandemic.
- Padhe Bharat Badhe Bharat : Library grant and Promotion of reading : In order to inculcate reading habit among students of all ages, strengthening of school libraries is being undertaken through provision of books by providing library grant for government schools, under the newly launched centrally sponsored scheme of Samagra Shiksha from 2018-19. The fund for library grant ranges from Rs. 5000/- to Rs. 20000/- based on the category of the school. An outlay of Rs. 630.51 Crore for the Year 2020-21 and an outlay of Rs. 716.13 Crore for the Year 2021-22, has been approved under Library Grant for Government Schools in States/UTs.
The old Guidelines on library grant have been revised this year. The present Guidelines dated 28th October 2021, emphasize on the promotion of reading as a whole apart from development of libraries and procurement of library books and the activities that can help achieve these goals. Further, the recommendations of New Education Policy, 2020 were also considered while framing the present guidelines.
- Khele India Khile India: Grant for Sports and Physical Education : Realizing the need for holistic development of children, under the Samagra Shiksha, Sports and Physical Education component has been introduced for the first time for encouragement of Sports, Physical activities, Yoga, Co-curricular activities etc.A provision has been made for government schools for sports grant of Rs. 5,000 for Primary schools Rs. 10,000 for upper primary schools and up to Rs 25,000 for secondary and senior secondary schools for meeting the expenses. An outlay of Rs. 642.33 Crore for the Year 2020-21 and an outlay of Rs. 822.19 Crore for the Year 2021-22 has been approved under Sports Grant for Government Schools.
Ministry has issued guidelines to States and UTs to ensure proper utilization of sports grant. These guidelines include an indicative list of age appropriate sports equipment for government schools. Sport specific equipment may also be chosen by the schools, based on availability of infrastructure in the school including availability of play field etc. States and UTs have been advised to encourage schools to include traditional/regional games of the respective State/Region. One responsible person/Physical Education Teacher (PET)/Teacher in charge in every school is to be given the responsibility to take care of the sports equipment and to maintain their stock position.
FIT India Campaign : Schools are actively participating in nationwide ‘Fit India Movement’ to inculcate physical activity / sports into daily life of citizens. The Department of Sports is organizing a nationwide ‘Fit India Movement’ to inculcate physical activity / sports into daily life of citizens. The Fit India Movement was launched by the Hon’ble Prime Minister on 29th August, 2019 at Indira Gandhi Indoor Stadium, New Delhi which was telecast live on Doordarshan. During the launch function Hon’ble Prime Minister administered a fitness pledge.
FIT India School Week is celebrated from 14th November 2021 till 12th December 2021. In all the four weeks total 288437 schools participated in various activities.
Fit India Star Rating: Department of Sports has prepared a ranking system according to the resources available in the schools of Fit India Schools to make fit India a people’s movement. Department of School Education and Literacy has written to all Principal Secretaries/Secretaries, School Education Department of States/UTs to apply for Fit India Star rating. As on 21st Dec 2021, 444531 Schools have awarded Fit India Flag, and 43074 Schools have applied for 3 Stars Rating and 13008 Schools have applied for 5 Stars rating.
FIT India Freedom Run 2.0 : FIT INDIA FREEDOM RUN 2.0 has been launched by Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports. We have requested all the Schools under all States/UTs/Autonomous Bodies to participate in large number in this event. FIT India Freedom run was launched on 13th August 2021 and culminated on 2nd October 2021
FIT INDIA Quiz 2021: for schools has been launched by FIT India Team on 1st September, its preliminary round has been conducted and results are awaited for the same. The objective of the quiz is to spread awareness about fitness among students.
FIT India Mobile App : has been launched on 29th August 2021 for Fitness Assessment based on the “Age-Appropriate Fitness Protocols – GOALS (Goals for Active Life Style)”.
- PM Poshan
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman (PM POSHAN), a modified version of the existing National Scheme for Mid-Day Meal in Schools (MDM) on 29th September, 2021. PM POSHAN Scheme covers all school children studying in I-VIII classes in Government and Government-aided schools. The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved the continuation of the scheme of PM POSHAN (erstwhile MDMS) in Schools for the five-year period 2021-22 to 2025-26 with the financial outlay of central share of Rs.54,061.73 crore for five years from 2021-22 to 2025-26. The CCEA also recommended the provision of Mid Day meal to Pre-primary class (Balvatika) alongwith the existing components.
After reopening of schools in many States and UTs, the Department has advised States/UTs to resume provision of hot cooked meal to eligible children attending schools by strictly adhering to the prevalent COVID protocols and social distancing norms. The States and UTs have also been advised to refer to detailed ‘SOP/Guidelines for Health and Safety protocols for Reopening of Schools and Learning with Physical/Social distancing’. These broad guidelines are aimed at helping State/district/block authorities to prepare for resuming the normal cooking and serving of Mid-Day Meal in schools with focus on food safety, health, and hygiene along with physical/social distancing.
With the approval of Hon’ble Shiksha Mantri, it has been decided to provide monetary assistance through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) of cooking cost component of MDM to all eligible children as per MDM norms for summer vacation period of 2021 only as a one time special welfare measure.
During 2021-22, Rs 4008.84 crore was released to States and UTs as central assistance and 30.95 lakh MT foodgrains was allocated to them.
Food Security Allowance: During 2021-22 With the approval of Hon’ble Shiksha Mantri, this Department issued advisories to States and UTs to provide Food Security Allowance, comprising of food grains and pulses, oil etc (equivalent to cooking cost) to enable children to meet their nutritional requirement in order to safe guard their immunity. Food Security Allowance has been provided to all enrolled children during closure of schools due to COVID pandemic and during summer vacations as a one time special measure for the first time in the history of the scheme. About 11.80 crore children are benefited under the scheme studying in 11.20 lakh school in the country.
School Nutrition (Kitchen) Gardens (SNGs): As a part of “Azadi Ka Amrut Mahotsav”, DoSE&L has decided to set up School Nutrition (Kitchen) Gardens (SNGs) and planting in an immense way during the monsoon season as it is easy to plant during this season due to heavy moisture content in the soil and air and the probabilities of survival of plants is more. School Nutrition (kitchen) Gardens (SNGs) utilizes the schoolyard to reconnect the students to a natural world and make them aware about the true source of their food and teach them valuable gardening, agriculture concepts and skills that integrate with several subjects such as math, science, art, health and physical education and social studies etc. The vegetables and fruits grown in these kitchen gardens are being used in the preparation of MDM. This offers an opportunity for students to eat freshly grown vegetables loaded with vitamins and minerals which are essential source of their physical and mental growth & development. Further, planting in approximately 11.20 lakh schools, the School Nutrition (Kitchen) Gardens shall be an initiative towards reducing the harmful effects of climate change as it reduces the “carbon footprint” of food by decreasing the number of miles it takes to get vegetables, fruits, legumes or pulses from the farm to PM POSHAN kitchen.
During COVID-19 pandemic, this Department has also held continuous consultations with the States and UTs at various levels in order to maintain healthy nutritional level of the children.
States and UTs have been requested to conduct social audit of the implementation of the Scheme. Several States have successfully conducted social audit.
Adult Education : A centrally sponsored scheme of Adult Education, Padhna Likhna Abhiyan (PLA) was approved on 25.04.2020 during the Covid-19 pandemic to impartFunctional Literacy to 57 lakh non-literates of 15 years and above age group in the country during F.Y. 2020-21.
Due to COVID-19 pandemic situation, the States/UTs faced a lot of difficulties to implement the scheme, therefore, the tenure of PLA Scheme was extended thrice by the DoE, MoE, first upto 31.07.2021, second upto 30.09.2021 and third upto 31.03.2022 so that the States/UTs could achieve the target of learners assigned to them.
Till 30th September, 2021, 25 States/UTs of the country conducted Assessment Test/Promotion process of learners and around 21.84 lakh learners appeared in the Assessment Test/Promotion process.
- National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme(NMMSS)
The ’National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme ’was launched in May, 2008 with the objective to award scholarships to meritorious students of economically weaker sections to arrest their drop out at class VIII and to encourage them to continue their studies at secondary stage. One lakh fresh scholarships are awarded to selected students of class IX every year and their continuation/renewal in classes X to XII for study in State Government, Government-aided and Local body schools all over the country. To maximise the reach of the NMMSS among the meritorious students of economically weaker sections, certain criteria, such as restrictions on Parental income from all sources and a minimum of 55% marks or equivalent grade in Class VII examination for appearing in Selection test for award of scholarship (relaxable by 5% for SC/ST students), have been set. There is reservation as per State Government norms.
Applications of eligible students, who register on the National Scholarship Portal (NSP),are verified by State Governments/UT Administrations who furthers end the proposals/ list of eligible beneficiaries to the Ministry. The Ministry scrutinizes the proposals and sanctions funds for disbursal of scholarships to students directly into their bank accounts through Public Financial Management System (PFMS) by Direct Benefit Transfer(DBT).
Achievement under Nationa lMeans-cum-MeritScholarship Scheme (NMMSS) for the periodJan.2021to Nov,2021
|
No.ofScholarships (Fresh*Renewal)
|
Amount Sanctioned (Rs.inCrore)
|
|
246888
|
249.35
|
- NFTW
NFTW is a Foundation to provide financial assistance to teachers, who applied through their respective States /UTs to avail the grant in the schemes of this Foundation which is under control of MoE, Department of SE&L and governed under Charitable Endowment Act, 1890 and Income Tax Act, 1961.
Financial assistance of Rs 2,30,00,000/- (Approx) has been processed during the year.
- National Awards to Teachers
- The National Awards to Teachers were first instituted in 1958 to recognize excellence and commitment of teachers in shaping the minds as well as future of the youth. From mid-60s, 5th September came to be the fixed date for the function on account of birthday of Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, former President of India. The award was to accord public recognition to meritorious teachers working in elementary and secondary schools.
The guidelines of the National Awards to Teachers Scheme were revised in the year 2018 in order to make the new scheme more transparent, fair, and reward meritorious teachers so that they could be held as examples and inspiration for other teachers. The features of the new scheme are as under:
- In the revised guidelines there is a provision for online self-nominations from teachers which are invited on education.gov.in.
- All regular teachers are eligible and no minimum years of service is required. This enabled meritorious young teachers to apply.
- The numbers of awards have been rationalized to 45+2, as against the earlier 378, thereby restoring the prestige of the awards.
- In addition, 2 teachers under Special Category could be selected from differently abled teachers etc., if any.
- No State, UT or Organization had a quota in the final selection. This encouraged them to compete for the awards truly at National level.
- The final selection is done by an Independent Jury headed by a retired Secretary, Department of School Education & Literacy from amongst nominations received from States/UT’s and Organizations, thereby ensuring that the role of these agencies was not diluted under the new scheme.
- The nominated teachers make a presentation before the Jury for final selection. This ensures that all of them are given an opportunity to share the work done by them.
In 2021, for the first time in the history of the National Awards to Teachers, high quality films of one minute duration on the exemplary work done by each one of the awardees have been made since 2018. The films have been shot on location in the respective schools of the awardees, artistically and succinctly capturing the wide gamut of innovative activities like promotion of joyful learning through art & theatre resource mobilization from community, use of free educational apps & ICT, development of school nutrition garden etc.
For the year 2021 the online self nomination process followed by 3 tier selection process at District, State and National level. The Hon’ble President of India conferred the awards to 44 Awardees through Webinar, due to COVID-19 pandemic situation, on 5th September, 2021 in New Delhi.
Miscelleneous
Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat Campaign
An illustrative list of suggested activities in accordance with NEP 2020 that may be taken up for Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat (EBSB) Programme in schools has been drawn up by the Department of School Education & Literacy and shared with States, UTs and concerned organizations .
All the States/UTs and Institutes under Department of Schools Education & Literacy have been requested to constitute EBSB clubs in their schools.
3.5 Lakh EBSB Clubs have been formed in schools in J&K, Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Uttarakhand, Tripura, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Odisha, Gujarat, Telangana, Kendriya Vidyalayas and CBSE etc.
Altogether 3.2 crore students from across the country have participated in EBSB activities during the year 2020-21. All States and Union Territories have been culturally mapped under EBSB.
Rashtriya Ekta Diwas: Rashtriya Ekta Diwas or National Unity Day-2021 has been observed in online mode this year. A national level story writing activity on the theme is also being hosted by the Department of School Education & Literacy at MyGov platform from 31st October, 2021-30th November, 2021.
Bhasha Sangam: Under the umbrella programme ‘Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat’, Bhasha Sangam programme is being conducted for promoting languages and linguistic harmony in schools through familiarizing learners with the 22 scheduled languages. About one hundred sentences in the 22 schedule languages of India are presented to learners on various themes and their lived-in contexts.
Bhasha Sangam programme was held on 1st November, 2021, through launch of a mobile app and 22 booklets (QR coded with audio and Indian Sign Language) with the aim of learning of 100 sentences in the 22 scheduled Indian languages to facilitate listening, comprehension and practice speaking of these languages.
Kala Utsav: National Level Kala Utsav-2020 has been organized from 11 January to 22 January 2021 at national level through online mode; in which a total 574 students from different States/UTs participated.
Matribhasha Diwas Celebration: The international mother tongue day-2020 was celebrated in all the schools in which 2,16,95,954 students participated from across the country.
Online Series on Indigenous Sports: During the closure of schools, an online series on Indigenous games of India was organized in coordination with Fit India Cell, Ministry of Sports and Youth Affairs.
Book on Unity in Cultural Diversity: A book namely “Unity in Cultural Diversity” prepared by the NCERT has been shared with all the States for further dissemination.
Vidyanjali: Hon’ble Prime Minister launched Vidyanjali programme on 7th September, 2021, with the aim of strengthening schools and improving the quality of school education through community, CSR and private sector involvement across the country. Vidyanjali portal acts as a facilitator by connecting contributors directly to the schools. The effort is to bridge knowledge / skill / human resource and infrastructure gap in the schools by tapping the potential available outside the government. This is not to substitute the government responsibility, but to compliment, supplement and strengthen government efforts to reach the last mile in the best possible way.
With the help of Vidyanjali – alumni of educational institutions, serving and retired teachers, scientists, government/semi government officials, retired armed forces personnel, self-employed and salaried professionals, homemakers, persons from the Indian diaspora and any other organisation/group or company may volunteer to participate in schools of their choice by sharing their knowledge and skills or by contributing assets/material/equipment.
The broad categories of contribution include services/activities, sponsorship activities as well as assets/materials such as basic civil infrastructure, basic electrical infrastructure, digital infrastructure, equipment for extra-curricular activities & sports, yoga, health and safety aids, teaching learning materials, maintenance & repairs, office stationery/furniture/support services/needs etc.
Depending on the request raised by the schools, a Volunteer, based on his/her area of expertise/interest or assets & materials, expresses his/her interest to partially/ fully contribute to the schools’ request. So far 99888 schools have onboarded and 11750 volunteers have registered on the Vidyanjali portal. Volunteers have expressed interest in several areas such as subject assistance, mentoring of gifted children, teaching vocational skills, sponsoring projector, laptop and library for schools etc.
Statistical Profile of School Education in India
Performance Grading Index (PGI) : The Performance Grading Index (PGI) developed by Department of School Education & Literacy(DoSEL) aims to assess the relative performance of the all the State/UTs in a uniform scale to encourage State/UTs to perform better. The PGI has been conceptualized as a tool to motivate States and UTs to adopt best practices followed by the top performing State. The PGI has five domains with seventy (70) indicators carrying a score of 1000. The PGI: State report for the year 2019-20 was released in June 2021. The PGI reports can be viewed in public domain in https://www.education.gov.in/en/statistics-new?shs_term_node_tid_depth=391&Apply=ApplyPGI Report 2019-20 (English)/(Hindi), PGI Report 2018-19 (English)/(Hindi) etc. As a logical next step of the PGI: State, an 83 indicator based PGI: District has been developed to grade the performance of all districts in school education. The online data collection and compilation mechanism for PGI: District has been developed and launched. The compilation of data for the year 2018-19 and 2019-20 is under process. The PGI: District is expected to help the State education departments to identify gaps at the district level and improve their performance.
UDISE PLUS: The “Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE) Plus developed by DoSEL collects data from more than 15 lakh schools and nearly 26.5 crore students on various indicators on school education on an annual basis. Data in UDISE Plus is filled directly by the schools online in the portal viz., http://udiseplus.gov.in/# . UDISE Plus data are validated and verified at Block, District and State level for ensuring its authenticity. The UDISE+ report for 2019-20 has been released in July 2021 can be accessed online at http://dashboard.udiseplus.gov.in. The compilation of data for the reference year 2020-21 is under process.
Examination Result: The DOSEL complies data on results of Secondary and Higher Secondary Examinations conducted by the various examination boards in the Country. The information is disseminated with a view of having a holistic datasets reflecting the Board Examination Results for both Secondary and Higher Secondary levels. The Examination Result for the year 2020 has been published by the DoSEL in October 2021, which is available in the link https://www.education.gov.in/en/statistics-new?shs_term_node_tid_depth=380&Apply=Apply.
Data Governance Quality Index (DGQI): The NITI Aayog has developed DGQI platform in 2020 for assessing the data preparedness of the Ministries/ Departments in respect of Central Sector/Centrally Sponsored Schemes. The DGQI assess the Ministries/ Departments of Government of India on a uniform scale of 0 to 5. In DGQI 1.0 ( 2020), DoSE&L was assigned the score of 2.95 out of 5. NITI Aayog has carried out DGQI 2.0 exercise in 2021 wherein data in respect of 3 schemes of DoSEL viz., Samagra Shiksha, Mid Day Meal and National Means cum Merit Scholarship have been considered for assessment. In DGQI 2.0 draft report, DoSEL has improved its score from 2.95 to 4.28 making remarkable improvement in 2021.
Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan
1. Inauguration of Digital Language Lab
Smt Savita Kovind, First Lady of India, inaugurated the Digital Language Lab at Dr Rajendra Prasad Kendriya Vidyalaya, President’s Estate on 7th January 2021. The event was attended by Hon’ble Minister of Education as well.
2. Inauguration of new building of KV No. 4 Korba
A newly constructed building for KV No. 4 Korba (Chhattisgarh) equipped with all modern facilities was inaugurated on 21.01.2021 by Hon’ble Shiksha Mantri Dr. Ramesh Pokhariyal Nishank.
3. Inauguration of new building of KV Siddharthnagar
A newly constructed building of Kendriya Vidyalaya Siddharth Nagar was inaugurated on 23rd September 2021 by the Hon’ble Education Minister Shri Dharmendra Pradhan. The new building will facilitate the all-round development of students with its modern amenities.
4. Visit of Hon’ble PM of Denmark
Ms. Mette Frederiksen, Hon’ble PM of Denmark, has visited Kendriya Vidyalaya Sec. 8, RK Puram in Delhi on International Day of the Girl Child to discuss the lives and dreams of the girl students.
5. Chief of Air Staff presents MiG-21 to his alma mater
Air Chief Marshal Rakesh Kumar Singh Bhadauria, Chief of Air Staff visits his alma mater on 6.9.2021 and presented the air frame of a decommissioned MiG-21 Aircraft to KV Sec 47, Chandigarh. Many of his classmates were also present on the occasion along with KVS Officials.
5. Pradhanmantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar-2021
Two students of Kendriya Vidyalayas were awarded with Pradhanmantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar-2021
6. Guinness World Record
TGT (WE) at KV Tirumalagiri, made a successful entry to Guinness Book of World records through ‘Largest display of Origami Peacocks’. He displayed 1776 peacocks and was awarded GWR Record holder certificate.
7. National Award to KV Teacher
Govt. of India felicitates and awards eminent teachers from different organizations on Teachers’ Day every year. From KVS this Award was conferred upon TGT (Librarian) of Kendriya Vidyalaya Pattom for the Academic Year 2020-21.
8. Pariksha Pe Charcha-2021
In this year’s Pariksha Pe Charcha program conducted on virtual mode, class 10th student of Kendriya Vidyalaya IIT Guwahati, Km. Krishti Saikia got an opportunity to ask exam related question to the Hon’ble Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi. Her question was on how to reduce the generation gap between the new generation and the parents. The Prime Minister answered this question in detail and also praised Krishti for her good Hindi, despite having a different mother tongue.
9. Highest Exam Result in the academic year
Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan has achieved the highest ever result in the CBSE examinations of class 10th and 12th. While 100% (rounded off) students passed in class 10th board exam, 99.99% students passed in class 12th.
11. Details of Kendriya Vidyalayas opened from 01.01.2021 till date
A total number of 3 Kendriya Vidyalayas have been opened till date. As on date KVS is a vast chain of 1248 KVs including three abroad (Moscow, Kathmandu & Tehran)
|
S.No.
|
KV Name
|
State
|
|
1
|
Sadalgah
|
Karnataka
|
|
2
|
IIT Ropar
|
Punjab
|
|
3
|
Bilaspur
|
Haryana
|
12. Details of KV School Buildings Completed During 2021
A total number of 14 Kendriya Vidyala Buildings were completed during the year 2021. They are in Pandurana (Madhya Pradesh), Miao (Arunachal Pradesh), Sec- 28 Rohini (Delhi), Chaurai (Madhya Pradesh), Tonk (Rajasthan), Jalore (Rajasthan), Koppal (Karnataka), Chikodi (Karnataka), No. 2 Chhindwada (Madhya Pradesh), Chakur (Maharashtra), Kanhagad (Kerala), Budayan (Haryana), Nagaur (Rajasthan), Sidhharthnagar (Uttar Pradesh)
NAVODYA VIDYALAYA SAMITI
CBSE Class XII results: A total of 32943 students from 557 JNVs appeared in All India Senior School Certificate Examination – 2021 (Class XII). A total of 32925 students passed in the examination(99.94%) with 32766 students securing First Division(99.46%). 543 JNVs produced 100% pass results and 44 students secured Centum.
UPSC 2020: 27 JNV Alumni were selected for Civil Services in UPSC 2020
In JEE Main 2021, 4292 students of JNVs qualified out of 10247 students appeared (41.89%).
In JEE Advance 2021 1121 NVS students qualified out of 2770 students appeared (40.47%).
In NEET 2021 14025 students of NVS qualified out of 17520 appeared (80.05%)
Joint Music Competition NVS and KVS : NVS secured 1st and 3rd positions in Joint Music Competition between NVS and KVS held at National Level on 9th of September, 2021
INSPIRE Manak Awards: In INSPIRE MANAK Award 2019-20, out of total 60 selected students at National Level, two (2) students are from NVS.
Khagolshala Asteroid Search Campaign (KASC): JNV students had done preliminary discovery of 384 asteroids under this campaign from January to March in 2 Phases of the program. Total 9 Asteroids (Provisional Discovery) from 8 teams(16 students) of JNVs were confirmed by International Astronomical Search Collaboration (IASC) and International Astronomical Union.
International Admissions: 3 students from NVS got Admission in International Universities in 2021
Under the “Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram” (PMJVK) of Ministry of Minority Affairs all classrooms (total 1173) have been converted into Smart Classrooms in 99JNVs (including one virtual class in each JNV)
Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs declared the result of 23rd National Youth Parliament. Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Alleppey, Kerala from Hyderabad Region stood first at National level and they have bagged Nehru Running Shield and a Trophy.
National Council Education Research and Training
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an apex resource organization established in 1961 by the Government of India to assist and advise the Central and the State Governments in the formulation and implementation of their policies and programmes in the field of education, particularly school education and teacher education. It provides academic and technical support for qualitative improvement in school education and undertakes programmes related to educational research, development, training, extension, international cooperation, publication and dissemination of information.
National Curriculum Framework: As a follow-up of the National Education Policy -2020, the NCERT has initiated the groundwork for preparing National Curriculum Framework for School Education, National Curriculum Framework for Early Childhood Care, National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education and Education and National Curriculum for Adult Education. In order to develop the NCFs on time, the activities initiated are: identified 25 themes from the NEP,2020 for the Focus Groups, shared the strategy document with all the States/UTs, constituted internal committees at NCERT to speed up the process, initiated the process of the development of tech-platform to roll out questionnaires and templates, rolled out MyGovSuvey questionnaire, constituted National Steering Committee (NSC) and conducted first meeting of the NSC, identified national-level nodal officers for each State/UT and initiated the process of District level consultations on pilot basis.
Manodarpan :As part of “Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan”, Manodarpan programme conducts by NCERT to provide psycho-social support to students, teachers and families for mental health and emotional well-being during the times of COVID-19 and beyond. Under the initiative, a webpage has been created on the website of the MoE. Also, National Toll-free Helpline (8448440632) is set up to provide tele-counselling services to the students (across schools, colleges, and universities), their parents and teachers to address their mental health and psycho-social issues. As per the direction of MoE, ‘ManodarpanCell’ was established at NIE, NCERT, New Delhi in October 2020. Under Manodarpan, several activities such as running of the tele-helpline, organizing webinars, live interactive sessions ‘Sahyog’ with practicing counsellors, celebrating of ‘Mental Health Week’ in schools and colleges, etc. were conducted.
PM eVidya: PM eVidya is an initiative by the Ministry of Education, Government of India to facilitate learning of the children. It offers multifarious educational resources in multi-platform mode viz., digital / online, TV, radio, community radio, podcast, etc. DIKSHA,One Nation-One Digital Platform, hosts plenty of multi-modal education contents free for the use of learners, teachers and other stakeholders working in the field of education. DIKSHA has been adopted by almost all the States/UTs, central autonomous bodies/boards including CBSE. DIKSHA can be accessed by learners and teachers across the country and currently supports 31 Indian languages. Each State/UT leverages the DIKSHA platform in its own way, as it has the freedom and choice to use the varied capabilities and solutions of the platform to design and run programs for teachers, learners and administrators. NCERT entered into a MoU with ISLRTC under which sign language videos were developed jointly. About 610 ISL videos have been recorded and uploaded on DIKSHA. About 3,059 audio book chapters have been developed and uploaded on DIKSHA. DIKSHA also houses learning outcome-based contents for upper primary in the form of video, worksheets and info graphics. Many online quizzes were also used on DIKSHA by school students e.g., National Constitution Quiz with Ministry of Law and Justice, National Yoga Quiz, know your constitution quiz, Discover Gandhi Quiz, etc.
NCERT also delivered contents for students through 12 PM eVIDYA DTH TV channels (One Class, One Channel from classes I to XII), that delivers class-wise contents on 24×7 basis; these are linked to DIKSHA through QR codes. NCERT has geared up its TV and Radio programme production process and has developed a large number of educational audio video programmes based on NCERT curriculum for its dissemination under PMeVIDYA. As part of One Class, One Channel, 12 DTH TV channels has been started w.e.f. September 1, 2020 and curriculum based programmes are being telecast on 24×7 hours basis from classes 1-12 (a dedicated channel for every class). All the channels are carried by DD Free dish and some of the private cable operators also carry these channels. Contents of these channels are also available on Jio TV Mobile app. Curriculum based educational radio programmes are also broadcast on 230 Radio stations (including 18 Gyan Vani Radio Stations, 80 Community Radio Stations and 132 All India Radio Stations) and podcast on Jio Saavn Mobile app and on iRadio as podcast. Contents disseminated through telecast and broadcast are also available through DIKSHA portal and apps for learning in online mode as part of resilient and cohesive access to digital contents (NEP-2020).
NCERT initiated a webinar series focusing to orient teachers, students and other stakeholders on various ICT tools, digital initiatives at national level, emerging trends in educational technology, cyber safety and security, etc. A variety of sessions in English and Hindi has been conducted live which is simulcast through NCERT Official YouTube Channel live as well as 12 PMeVIDYA DTH TV Channels and Jio TV mobile App. Till June 2021 more than 446 live sessions of one hour each have been organised on ICT tools for teaching learning and assessment to realize the vision of Digital India (2015) and NEP, 2020. A repository of these presentations is also created for easy reference and can be accessed at https://ciet.nic.in/pages.php?id=webinar&ln=en.
Cyber safety and security guidelines: Safety concerns during online learning are considered seriously and NCERT has designed cyber safety and security guidelines for teachers, students, parents and schools and also has developed guidelines on cyber bullying in collaboration with UNESCO and ISEA-CDAC, MeitY. Online quizzes were conducted to orient various stakeholders in the safe use of technology. Guidelines can be accessed at https://ciet.nic.in/pages.php?id=booklet-on-cyber-safetysecurity&ln=en&ln=en.
ePathshala : ePathshala initiative of the Ministry of Education, GoI is for dissemination of Digital Books and eContents. Using ePathshala web portal (https://epathshala.nic.in/) and mobile app (Android, iOS, Windows), students, teachers, teacher educators and parents can access more that 696 digital books including 377 e-textbooks (classes I to XII) and 6,235 audios and videos of NCERT as free and open resources in various languages (Hindi, English, Sanskrit and Urdu). ePathshala (https://epathshala.nic.in/) portal having nearly 14.6 crores visitors and 49.1 lakhs app downloads.
NROER: The National Repository of Open Educational Resources (NROER) web portal is a storehouse of eContents for students, teachers, teacher educators and parents. About 19,723 eContents of NCERT and other collaborative partners are available on NROER for free in various school subjects (Classes I to XII). These curriculum-based e-Contents can be accessed by logging on to: https://nroer.gov.in/welcome NROER is having about 2.5 lakhs visitors and 9,000 unique visitors per day. These contents are also available on official YouTube channel of NCERT.
Vocational Education: Pandit Suderlal Sharma Central Institute of Vocational Education, Bhopal, a Constituent Unit of NCERT developed students’ textbooks for identified job roles under the scheme of Vocationalisation of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education introduced by the MoE, Government of India. The textbooks were developed for 52 job roles in 19 sectors under NSQF approved by Project Approval Board (PAB) and published 57 Student Textbooks in 19 sectors
Research Projects: NCERT has undertaken research studies in the priority areas of school and teacher education viz., Preschool Education, inclusive education, gender in education, syllabi and textbooks, social science, science, language education, ICT, educational psychology, etc. The Council has taken up block level research projects in different regions of the country.
Pre-service courses: Regular pre-service courses are being conducted in the Regional Institutes of Education of NCERT situated at Ajmer, Bhopal, Bhubaneswar, Mysuru and NERIE, Umiam. (i) Four-year integrated B.Sc.B.Ed., (ii) Two-year M.Sc.(Life Science) Ed. (iii) Four-year integrated B.A.B.Ed., (iv) Two-year B.Ed., (v) Two-year M.Ed. (vi) One-year M. Phil. in Education and (vii) Pre-Ph.D. course in education and one-year Diploma Course in Guidance and Counseling are conducted at the centres. As components of the pre-service course activities like multicultural placement, internship-in-teaching, working with community and field work were organized for students. The RIEs also have facilities for Ph.D. programme and RIE, Bhubaneswar is also recognised as a nodal centre for research in the field of education and for Pre-Ph.D. course in Education.
The International Relations Division (IRD), NCERT carries out various activities to promote international cooperation to facilitate exchange of information between NCERT and agencies and institutions abroad, signing of MoUs between NCERT and willing agencies/ institutions abroad. The Division hosts visiting delegations from abroad and facilitates cooperation in the areas of formulation of national education policies, development of national curriculum frameworks, organisation of pre-service and in-service teacher education programmes, formulation and implementation of programmes for vocational education, educational technology and facilitates the participation of faculty from the NCERT in international seminars, etc. MoUs have been signed between NCERT and the Florida Centre for Reading Research at Florida State University (FSU), USA and College of Education, University of St. Francis (USF), USA, Graduate Institute of Science Education (GISE), National Taiwan Normal University (NTNU), Curtin University, Australia, etc.
Textbooks: The NCERT continues with the publication of school textbooks, workbooks, supplementary readers, teacher guides, laboratory manuals, source books on assessment, exemplar problems in mathematics, research reports/monographs and educational journals. The NCERT textbooks are freely adopted by States under their nationalized textbooks programme. They are also widely accepted in schools affiliated to the Central Board of Secondary Education, Kendriya Vidyalayas, Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalayas, Tibetan Schools and many State government schools.
Inclusive Education: The Council works in the area of education of Children with Disabilities (CWD) and children belonging to socially disadvantaged groups, such as Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) and minorities. Implementation of an inclusive system of education for all assumes greater significance for systemic reforms especially in the context of the socially disadvantaged and the persons with disability. Several time bound projects and programmes were taken up by the Council in this area for the year 2021-22.
National Bal Bhavan
Outreach activities were carried out through online mode, where NBB Activity staff came up with encouragement programmers through motivational videos and educational programmes. These videos were uploaded at NBB’s YouTube channel as well as instructors cooperated with children through video chats and calls and NBB has received tremendous response from the regular students as well as non-regular students.
Some of the important online activities carried out by NBB are Virtual Exhibitions, Online activities of Bhartnatyam, Online activities on Vocal Music, Online activities on Folk Music, Folk Dance, Instrumental Music (Tabla), Instrumental Music (Sitar), Drama, Painting, Handicraft, Stitchery, Weaving, Clay Craft, Wood Craft, Physical Education, Home Management, Photography, Environment & Aquarium and Animal Corner, Aeromodelling, Astronomy, Museum, Computer and Radio & Electronics
National Institute of Open Schooling
Initiatives during Covid-19: NIOS initiated the innovative step of imparting live programmes every day on PM eVidya 10 and 12 channels for providing continued learning support for learners at Secondary and Senior Secondary level including Vocational Courses and Indian Sign Language based content.
Inclusive Education : Indian Sign Language as a subject: Indian Sign Language as a language subject introduced. This can be opted as a language subject in lieu of any other language by deaf/hard of hearing learners. Other learners (except deaf/hard of hearing learners) who wish to study Indian Sign Language can opt this as an additional subject.
NIOS delivers a one-hour live programme in Indian Sign Language twice a week on PM e-Vidya TV Channel 10
Sign language contents developed in 8 subjects at secondary and senior secondary level .These are available on Diksha Portal, YouTube channel of NIOS and on website
Talking books have been developed in 46 subjects at secondary and
senior secondary level
Bharatiya Jnana Parampara : NIOS has launched a new stream-‘Bharatiya Jnana Parampara’ (Indian Knowledge Tradition) for OBE Programme, Secondary and Sr. Secondary courses for reviving the Vedic Education, Sanskrit Language and Literature, Indian Philosophy and many other areas of ancient Indian knowledge.
Basic Literacy assessment of Neo-literates: NIOS has undertaken assessment of basic literacy for around 10 crore adult learners, out of which about 7.6 crore learners have been certified.https://nios.ac.in/nios-nlma-basic-literacy-assessment.aspx. Assessment is done across the country in 31 languages twice a year.
Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan (PMGDISHA): aims at enabling people to benefit from digitalization. This scheme is inclusive of gender, class and religion. Till now 1.1 crore learners have been certified under this initiative.
NIOS Education Project for Indian Army (NEPIA): NIOS signed an MoU with the Indian Army wherein Army Troops (Jawans), can complete their 10th or 12th certification from NIOS opting the subjects of their interests and requirements like Military History, Military Studies and Physical Education and Yoga.
Skill Training of Handicraft Artisans and their Children in collaboration with Ministry of Textiles (MoT): NIOS has so far conducted training of 300 Handicraft Artisans in Handicraft clusters, which includes both self learning and face to face. The practical training is provided along with wage compensation to the artisans while attending the PCP.
Certification of more than 9 lakhs ASHA workers(in collaboration with Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and NHSRC): 55 thousand have already been certified with 1500 District Trainers and State Trainers.
Integration of Vocational with Academic courses: All learners can take 4 academic subjects and 1 vocational course at Secondary and Sr. Secondary level.
Vocational Stream: Beauty and wellness, Agriculture and Animal Husbandry, Yoga and Naturopathy, IT & ITES
Academic Equivalency for ITI Learners through Credit Transer for Secondary and Sr. Secondary.
MoU with MSDE for Education of 9 lakhs non-literares and neo-literates through NIOS Open Basic Education for 370 Jan Shikshan Santhan.
NIOS has done various MoUs with State Govt’s and Ministries –
i) Food Safety Standards Authority of India (FSSAI): MoU was signed with the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, was signed on 22nd January 2020. The objective of the MoU is to integrate food safety and awareness content of FSSAI in NIOS curriculum and jointly develop courses on Nutrition and Food Safety to provide joint certification.
ii) MoU with Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya (KGBV), Gandhinagar: NIOS signed an MoU with Gujarat Council of Elementary Education in November 2019 for offering vocational skills to the girl students enrolled in the KGBVs. 168 KGBVs were accredited under the project to impart skill training to the girls in the area such as Beauty Culture, Basic Computing, Yoga, Indian Embroidery and Cutting Tailoring & Dress Making by the schools.
iii) MoU with State Govt of Bihar: Skill training of untrained health workers in the State of Bihar – A MoU between NIOS and the State Health Society, Health Department; Govt. of Bihar has been done to train 4 lakh untrained Community Health Workers of Bihar.
iv) MoU with NHM, Maharashtra: NIOS and National Health Mission, Public Health Department, Government of Maharashtra signed a MoU on 7th May 2019. This MoU is focused at offering Vocational programmes to the Health Service Providers of National Health Mission (NHM)through NIOS courses. The aim is to impart uniform, structured and quality training to the Multipurpose Health Workers (MPW) and Class III Male Health Workers. The course material in Marathi language for the learners is under process.
v) MoU with Indian Medical Association of India (IMA): NIOS and IMA has signed an MoU, the objective of which is to collaborate on projects and programmes related to the Health & Paramedical offered by NIOS.
vii) MOU with Prashanthi Balamandira Trust: A MOU signed by NIOS with Prashanthi Balamandira Trust on July 2021 for Accreditation of Schools for Secondary & Sr. Secondary Course. The trust has established 23 institutions in 18 districts of Karnataka and one in Telangana. Further it has plans to extent its activities in all the districts of Karnataka and other States too. Nearly 5000 boys and girls are receiving value-based education.
Digital Initiatives
Virtual Open School:Union Minister of Education unveiled the National Institute of Open Schooling’s (NIOS) “Virtual School initiative” on August 14, 2021.
Virtual Open School has been stared from 27th October 2021, about 62 classes of Secondary & Sr. Secondary in different subjects have been conducted successfully.
PM E-Vidya Programmes Transaction of Courses at Secondary and Senior Secondary level on PM e-vidya through live, interactive programmes on weekdays on e-vidya Channel 10 (Secondary) and e-vidya Channel 12 (Senior Secondary).
SWAYAM MOOCs have been developed using the four quadrant approach – text in PDF, a teaching video, self assessment exercises; and discussion forum. 20 courses are available on SWAYAM MOOCs at the Senior Secondary Level and 16 courses at the Secondary Level.
DIKSHA: NIOS is an active contributor to DIKSHA Portal. NIOS is continuously uploading digital textbooks of various courses at Secondary and Senior Secondary levels on this digital repository. At present 21 subjects (English Medium) at Secondary level and 32 subjects (English Medium) at Senior Secondary level contents were uploaded.
Audio and Video Resources: NIOS Audio/Video resources are available on the NIOS website www.nios.ac.in and youtube channel.
QR Code, E-pub and Mobile app: Academic Department is making an effort to introduce QR Code, E-pub and Mobile app for SLM in all courses in OBE Programme, Secondary and Senior Secondary level.
Awards and achievements: The NIOS won the prestigious UNESCO King Sejong Literacy Prize 2021 for ‘Enabling the Education of Persons with Disabilities through technology-enabled inclusive learning materials with special focus on Indian Sign Language-based content’.
The Regional Centre Gandhinagar, NIOS, 24 Study Centres have been Accreditated for Gujarati/Hindi/English medium for Secondary & Sr. Secondary Course for out of School Children (OoSC) under the scheme of Samagra Shiksha, Gujarat Council of School Education (GCSE).
Central Board of Secondary Education
(A) Curricular Initiatives
New Scheme of Assessment for the year 2021-22: CBSE has notified a scheme of biannual examination from the session 2021-22 with different online/offline alternatives in addition to internal assessments prescribed in the syllabus. The examinations will be held at the end of two terms each on half of the syllabus .The first term examinations of one-and-a-half-hour duration will be held during November-December 2021 internally at the schools of students using the question paper comprising only Multiple Type Questions developed by CBSE and in the presence of external supervisors appointed by CBSE. The second term examination will be held during March –April 2022 in external centers for a reduced duration of 2-hours. This would have descriptive questions. After the notification of this scheme on the month of July 2021, schools have started teaching on the basis of divided syllabus.
Launch of Structured Assessment for Analyzing Learning(SAFAL)forGrades3,5and8 : CBSE launched Structured Assessment for Analyzing Learning (SAFAL), a competency- based assessment forGrades3,5and8 to assess the progress of foundational skills and basic learning outcomes/competencies among students. SAFAL, as a diagnostic assessment, will provide developmental feedback to schools and teachers to improve teaching-learning without additional examination pressure on students. It has been designed to help students, parents, and teachers to track learning progress throughout the school years and not just in Grades 10 and 12. SAFAL results will not be used in any manner by schools for promotion of students to the next grade. SAFAL will be conducted on a pilot basis in CBSE schools for students in Grades 3, 5 and 8 during the academic year 2021-22,in key curricular areas of Language, Mathematics, and EVS/Science.
Launching of CBSE Foundational Literacy and Numeracy(FLN)mission inline with NIPUN BHARAT Guidelines in CBSE Schools : For the implementation of NIPUN BHARAT in its schools,CBSE in association with Central Square Foundation has launched the Professional Development Course on FLN for the capacity building of teachers. The courses have been designed with an aim to bridge the learning gap in early grades, develop the capacity of teachers to understand concepts in the FLN domain and equip them with tools and resources to help them in the classrooms. The Board has also created a microsite called FLN corner and it can be accessed at http://cbseacademic.nic.in/fln/
A question bank of 500 competency-based questions for each grade for grades 1 to 5 available at CBSE FLN microsite.
Launch of CBSE SQAAFramework or School Quality Assurance and Assessment Framework of CBSE: CBSE has been mandated to act as Standards Setting Authority (SSA) for Kendriya Vidyalayas and Navodaya Vidyalayas and frame parameters against which these schools can be assessed for quality interventions. The quality assessment framework launched enable schools to evaluate themselves against the defined standards and embed transformational change and provide the schools with qualitative benchmarks around which they can charter their own self-improvement. Standards have been prepared in different 7 areas of school functioning Curriculum, Pedagogy and Assessment (40% weighting), Infrastructure(10%W), Human Resources(10%W), Inclusive Practices(10%W), Management & Governance(10%W), Leadership(10%W), Beneficiary Satisfaction(10%W). CBSE has initiated a Pilot Study with different schools from across the country including KVs,JNVs has started which will be concluded in January 2022 and orientation programme for schools to sensitize them on the School Quality Assessment Standards Framework are organized. SQAA will be linked to the extension of affiliation from the year 2022.
(B) Major Conferences /Awards
CBSE Honour for Excellence in Teaching and School : Hon’ble Minister of State for Education on September 21,2021 felicitated 22 Teachers and Principals of CBSE affiliated schools in and outside India for demonstrating Excellence in Teaching and School Leadership. The awards for the year 2020-21 were given during an online ceremony in the presence Chairperson CBSE and SecretaryCBSE. The 22 awardees are Primary, Middle, Secondary and Senior Secondary Level teachers, who have not only contributed immensely with their innovative practices, but also stood the challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic and ensured uninterrupted teaching in online modes and reached out to students.
(C) Student Enrichment Activities
-
- Aryabhata Ganit Challenge(AGC) 2021 : As part of celebrating Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav (lndia@75), CBSE organized Aryabhata Ganit Challenge(AGC)-2021 to enhance mathematical abilities among students.Theme of theAGC-2021wasIndia’sMathematicalHeritage.In order to reach
Out to maximum students across the country, the Board hosted the Aryabhata Ganit
Challenge on MyGov and DIKSHA platforms this year. This challenge was available from 31th August 2021 to 30th September 2021. Students from class 8 to 10 irrespective of the Board are eligible to participate in this challenge.
(ii) Activities for Awareness in Students regarding India’s Freedom Struggle and Singing of Rashtragaan as a part of AzadiKaAmrutMahotsav : CBSE requested its schools to participate in all the events including singing of Rashtragaan that are being organized to commemorate the75thAnniversary of India’s independence under Azadi Ka Amrut Mahotsav (AKAM) by conducting activities like Postermakingcompetition,Paragraphwritingaboutplacesrelatedtofreedomstruggle Role play, Storytelling by grandparents and Quiz etc.
(iii) Adolescent Peer Educators Leadership in LifeSkills, Health and Wellbeing Programme : CBSE has planned to initiate and support the Adolescent Peer Educators Leadership Program for enriching Life Skills, Holistic Health and Wellbeing of its students in collaboration with Expressions India. With the conceptual framework of physical, mental and interpersonal development, certain overarching themes have been identified for taking forward the first phase of implementation of this initiative through a series of orientation programmes. Schools shall nominate four senior students (Peer Educators) – two each from class IX and XI to participate in the comprehensive orientation program and one Teacher and the School Counsellor/ Wellness Teacher to support the 4 peer educators.
(iv) CBSE Reading Challenge 3.0
With a focus on promoting Reading Literacy among the learners, CBSE organised The CBSE Reading Challenge 3.0 for students of classes 6th to 10th for English and Hindi languages. This challenge is available on the DIKSHA platform from 22/11/2021 to 31/12/2021.Students from class 6 th to 10th are eligible to participate in this challenge. The students of schools not affiliated to the CBSE can directly access the course on DIKSHA platform. All students who complete the course would be provided a participation certificate. Participation certificates will be issued online on the DIKSHA platform itself upon completion of the course.
-
- Azadi ka Amrut Mahotsav: DoSEL- DoP 75 Lakh Post Card Campaign: As part of the ongoing celebrations of Azadi ka Amrut Mahotsav (AKAM), the Department of Posts (DoP), Ministry of Communication, along with the Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Education, has beenorganizingthe’75 Lakh Post Card Campaign’, from December 1-30,2021 for the students of classes 4th to12th of all schools affiliated to CBSE. The students are required to write a Post Card to Hon’ble Prime Minister of India on any of the two topics- “Unsung Heroes of Freedom Struggle” and “My vision for India in 2047”. The School Heads will shortlist a maximum of 10 post cards and upload on the CBSE portal/MyGov portal. Remaining post cards will be handed over to the local Postal Authorities. At CBSE National Level, 75 best post cards will be selected and be forwarded to DoP for participation in the final event to be held in the third or fourth week of January, 2022.
-
- VeerGatha : In order to disseminate the details of acts of bravery and the life stories of the brave hearts among the students, Department of School Education& Literacy and the Ministry of Defence organised the Veer Gatha Project from 21st October to 20th November 2021. As part of Veer Gatha Project, till 30th November 2021,the schools submitted best selected projects on gallantry award winners prepared by the students. After the regional level evaluation 25 best projects will be selected jointly from CBSE schools and State/UTs. These will be awarded by the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and Ministry of Education (MoE) on the forthcoming Republic Day i.e., on 26th January, 2022. Total19142 Entries were received from CBSE schools. 8,03,978 students of CBSE schools participated in the Veer Gatha Project. Evaluation is under- process.
Publications
- Reading Literacy: Practice Book for Students : the Board has developed and released the book Reading Literacy: Practice Book for Students for English. This practice book provides students of classes7- 10 with an opportunity to engage with a variety of texts in a self-learning mode. It will help students to learn the nuances of the language in an innovative, engaging and functional manner. The five units of this practice book are an eclectic mix of subjects ranging from food, travel, sports to our glorious heritage. The book presents a wide variety of authentic reading materials such as movie reviews, posters, quotations, cartoons, blogs, Instagram posts and more. It provides a rich reading experience to the students. These themes have been carefully curated keeping in mind the interests of the learner and the larger educational goals.
(ii) Handbook of Assessment and Evaluation : The Board in collaboration with Azim Premji University, Bengaluru and Central Square Foundation has developed the Handbook of Assessment and Evaluation: Best Practices in Item Design and Test Development. This handbook will help teachers of all subjects to design test items that are a valid and reliable measure of the student learning .Some of the intended objectives of this handbook are to: Provide guidance for test developers who create questions or tasks for learning assessments; Elaborate the role of learning frameworks for item writing, characteristics, and development of high-quality assessment instruments; and provide inputs construction of marking guides. This handbook breaks down the process of developing assessments into well defined, easy to comprehend modules which would help teachers to design accurate test items for testing varied competencies. The book is available on CBSE Academic website at the link http://cbseacademic.nic.in/web_material/Manuals/Assessment-Evaluation_handbook.pdf.
(iii) CTET Question Paper Anaysis : In line with the vision and recommendations of NEP2020,the Board initiated a study where a qualitative and quantitative review of the CTET papers..This review has substantiated the need to streamlining the test paper development process of CTET examination.
The syllabus was redefined to a detailed framework that articulates competencies which assess both content knowledge and pedagogical content knowledge. Further, a handbook for experts/ item authors was developed.
The following publications were developed in this process:
-
- CTET2020:StudyReport
- CTET2021:StudyReport
- Test Development Process:Handbook for Experts
- Competency Framework:Paper1
- Competency Framework:Paper2
This work was done in collaboration with Azim Premji University and Central Square Foundation.
(iv) Report of the Committee to Formulate Guidelines to Design Question Paper for The Term I Board Examinations of CBSE (2021-22) : Due to school closure and other restrictions imposed during the COVID 19 pandemic in the academicsession2020-21,and subsequent tsecond wave since April 2021,theCBSE had to cancel 2020-21 Board examinations. The CBSE further announced a Special Scheme of Assessment for Board Examinations for Classes X and XII for the session2021- 22 that included 02 term examinations. A committee of experts and representatives from academia, research, testing organisations and administrators was constituted in July2021 to formulate guidelines for test design and development for Term1 and Term 2 of the session 2021-22. Work was completed and the interim reports were shared earlier in August 2021.
Psychosocial Well Being
The CBSE Counselling Program: CBSE Counselling is an annual flagship program of the Board, which aims tofacilitate different categories of secondary and senior secondary students at national and international level through free of cost pre and post exam counselling.
Traditional and advance modes of communications and outreach are adopted to achieve this very objective. CBSE started this pioneering community work 23rdyears ago in 1998 by initially offering telephonic counselling, which now has expanded into different modes and verticals:
Interactive Voice Response System(IVRS) : CBSE has been providing the facility of IVRS on a toll-free number. The students/parents/stakeholders can obtain pre-recorded useful information on tackling board exams which included tips for better preparation, time and stress management, FAQ’s along with live tele-counselling services.
Counselling for Differently Abled Students : CBSE also arranges counselling facility for differently abled Students. Experts are available to attend to the queries throughout this period.
Counselling through Audio-Visual Presentations : Audio-visual presentations were provided on CBSE website on various topics relevant to students as well as parents like Aggression, Internet Addiction Disorder, Depression, Exam Anxiety, Specific Learning Disability, Substance Use Disorder, and Life Skills.
Podcasts : Podcasts and other support material for students, parents and the public were also created and made available. Queries of the students were responded favourably and quickly through e-mails of the Board.
Social Media Engagements: YouTube, Facebook and Instagram platforms were utilized for promoting healthy practices, sharing important messages and connecting with students in a proactive way.Tips and FAQs were also shared on these platforms for the benefit of the students.
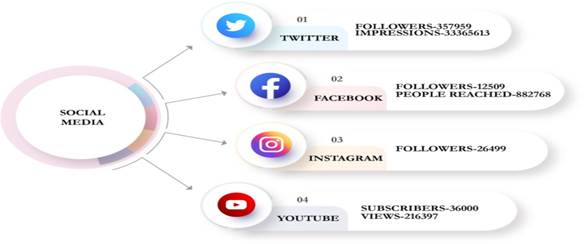
Public Responsiveness and Outreach: With the emergence of Social Media in recent times and growing public involvement and interest in this sphere, the Board has proactively created Social media Platforms on YouTube, Twitter, Facebook and Twitter perceiving its importance and utility for wider connectivity & communication with Board’s stakeholders.
Social Media Upsurge: CBSE social media handles have emerged as authentic sources of information for the public. During Lockdown period, there has been a remarkable increase in the number of followers and subscribers.
Monitoring of RTI and Public Grievances Redress : CBSE,in its drive for public facilitation,has aligned public grievance redress mechanism and information disclosure processes under RTI Act 2005 with online systems to ensure transparent and quick response. The Board proactively monitors and facilitates the online and offline RTI and public Grievance settlement.
Public Grievance Settlement under COVID Category : A special CORONA Category was made for grievances pertaining to COVID-19 and the Public Grievances received under this special category were replied within 03 days.













You must be logged in to post a comment.