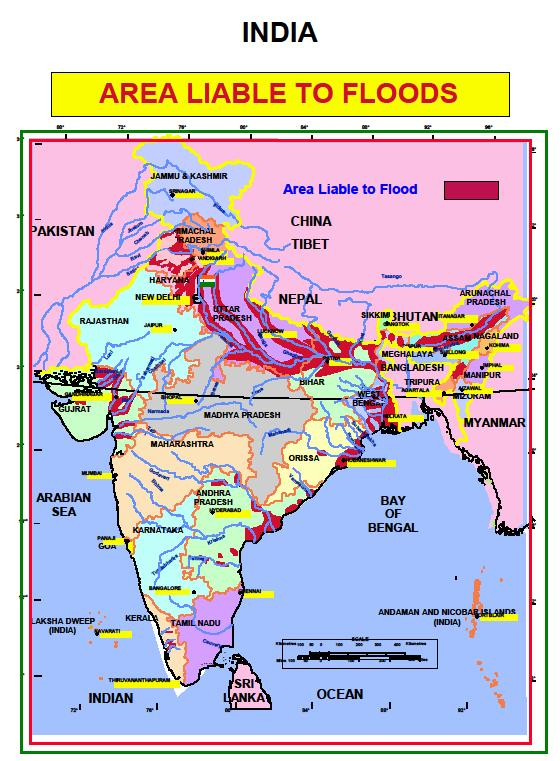
Before, During & After the Flood
Before
To prepare for a flood it is important to:
- Remember, if you decide to build your home in a flood plain, you should elevate and reinforce the home.
- Keep your furnace, water heater, and electrical panel elevated if you are in an area susceptible to flooding.
- Construct barriers to keep flood waters from entering your home.
During
If a flood is likely in your area, you should:
- Listen to the radio or television for information.
- Be aware that flash flooding can occur. If there is any possibility of a flash flood, move immediately to higher ground. Do not wait for instructions to move.
- Be aware of streams, drainage channels, and other areas known to flood suddenly. Flash floods can occur in these areas with or without such typical warnings as rain clouds or heavy rain.
If you must prepare to evacuate, you should do the following:
- Secure your home. If you have time, bring in outdoor furniture. Move essential items to an upper floor.
- Turn off utilities at the main switches or valves if instructed to do so.
- Disconnect electrical appliances. Do not touch electrical equipment if you are wet or standing in water.
If you have to leave your home, remember these evacuation tips:
- Do not walk through moving water. Six inches of moving water can make you fall. If you have to walk in water, walk where the water is not moving. Use a stick to check the firmness of the ground in front of you.
- Do not drive into flooded areas. If flood waters rise around your car, abandon the car and move to higher ground if you can do so safely. You and the vehicle can be quickly swept away.
Driving in a Flood
The following are important points to remember when driving in flood conditions:
- Six inches of water will reach the bottom of most passenger cars causing loss of control and possible stalling.
- Twelve inches of water is enough to float many vehicles.
- Two feet of rushing water can carry away most vehicles, including sport utility vehicles (SUV’s) and pick-ups.
After
Recovering from a flood requires extreme care. After a flood, be sure to:
- Find out if the water supply is safe to drink before consuming water.
- Avoid flood waters, as they may be contaminated. Also, avoid moving water.
- Driving is especially hazardous after a flood. Do not drive through flood waters or in areas where the water may have receded. Areas where the water has receded can be fragile and susceptible to collapsing under the weight of your vehicle.
- Only return home after authorities have instructed you to do so.
- Do not enter a building surrounded by flood waters.
- Be very careful when entering a building damaged by flood waters, as hidden damage is likely and can be extremely dangerous.
- Be sure to repair damaged sewage systems, as these can cause serious health risks.
- Clean and disinfect everything that got wet during the flood because flood waters may be contaminated.


















You must be logged in to post a comment.