Scheduled Tribes (ST) constitute approximately 8.6 percent of population of India numbering around 10.4 crores. There are over 705 Scheduled tribes notified under article 342 of the Constitution of India. In keeping with the vision of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi of ‘Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas’, the Government of India has focused on development of tribes and conservation of their heritage and culture as a priority.
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs in line with this vision and its enduring commitment for welfare of tribals geared itself to ensure sectoral development through enhanced allocation of financial resources, convergence of efforts, re-engineering of planning and implementation mechanism of the Ministry.
The budget of MoTA also increased from Rs. 3850 crores in 2014-15 to Rs. 7484 crores in 2021-22. This enhanced availability of resources has enabled the Ministry to chart a new progress path with greater commitment to ensure holistic development of tribal communities.
The major highlights of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs during the year 2021 are as follows:
- Cabinet approves declaration of 15th November as Janjatiya Gaurav Divas
The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi has approved declaration of 15thNovember as Janjatiya Gaurav Divas dedicated to the memory of brave tribal freedom fighters so that coming generations could know about their sacrifices about the country.
The date is the birth anniversary of Sri Birsa Munda who is revered as Bhagwan by tribal communities across the country. Pursuant to the speech of Prime Minister on Independence Day of 2016, Government of India has sanctioned 10 tribal freedom fighter museums across the country. Tribal Freedom
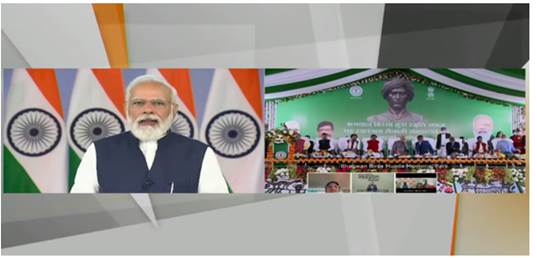
- Inauguration of Bhagwan Birsa Munda Museum in Jharkhand by Prime Minister
Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, inaugurated the Bhagwan Birsa Munda Tribal Freedom Fighters Museum and Park. Congratulating citizens of the state and the tribal society, PM Modi dedicated the Birsa Munda Memorial Udyan and Museum to the nation. A 25-feet tall statue of Birsa Munda was installed on the premises. “The project has been developed, in association with the Jharkhand government,”


It demonstrates the way tribals struggled to protect their forests, land rights, their culture and displays their valour and sacrifices, which is vital for nation-building.
- Prime minister Shri Narendra Modi laid foundation stone of 50 new Eklavya Model Residential Schools on occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Divas as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav
On the occasion of Janjatiya Garav Divas Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the construction of 50 new Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRSs) in 27 districts of 7 States and 1 UT through virtual mode from Bhopal at an event to commmeorate Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav (India @ 75). The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has been making continuous efforts in the direction of welfares of the tribal community; education being one of its key areas of intervention. The presently held stately stone laying foundation event marks the indomitable spirit of the Ministry aiming to niche education as a powerful driver for tribal students to pave the roads for future success and accomplishments.
- Minister Shri Arjun Munda and MoS Shri Bisheshwar Tudu laid the foundation stone of 11 EMRS in Jharkhand and Odisha.
Shri Arjun Munda and MoS Shri.Bisheshwar Tudu laid the foundation stone of 11 EMRS in Jharkhand and Odisha between July and September 2021. Total 84 EMRS foundation stones were laid during 2021; out of which foundation stone for 50 EMRS was laid by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, total 27 EMRS foundation stone was laid by Tribal Minister Shri Arjun Munda and MoS Shri Bisheshwar Tudu. Other than these, 7 foundation stone of EMRS was laid by State Ministers.
639 EMRSs have been sanctioned, which include 288 under the old scheme and 351 in the new scheme. There are 367 functional EMRSs across the country with around 85,232 students currently enrolled. The construction is under progress in 173 EMRSs, out of which 66 are in the old scheme and 107 are under the new scheme.
These schools are envisaged to be brought at par with Navodaya Vidyalayas. National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) as an autonomous body under the Ministry has been set up to provide overall support and policy directions to the schools in order to bring uniformity in the administration of the schools. The State/UT EMRS Societies at the State/UT level have been set up for day-to-day Administration and Management of the schools.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs organized Janjatiya Gaurav Saptah
The Government of India has announced 15th November, the Birth Anniversary of Bhagwan Birsa Munda as ‘Janjatiya Gaurav Divas’ to pay tribute to the sacrifices and contributions of tribal freedom fighters and for the preservation of cultural heritage and promotion of Indian values of valour, hospitality and national pride.
More than 125 events / activities were organized during the week-long Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav celebrations from 15th to 22nd November in various parts of the country to mark the Iconic Week to remember the great unsung tribal heroes who have sacrificed their lives and contributed to nation-building.
- Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah lays foundation stone for Rani Gaidinliu Tribal Freedom Fighters Museum at Luangkao village in Manipur
The Union Minister of Home Affairs and Minister of Cooperation, Shri Amit Shah, laid the foundation stone of the ‘Rani Gaidinliu Tribal Freedom Fighters Museum’ at Luangkao village, in Manipur’s Tamenglong district. The museum will inspire the youth of the country in dedicating their service to the nation apart from realizing the spirit of the freedom struggle.
Addressing on the occasion the Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah said that “It has been 75 years since the country achieved independence from the British, and the country has a strong commitment to become a superpower of the globe while celebrating its 100th year of independence 25 years later,”.
The Union Home Minister also remembered the life and sacrifices made by Rani Gaidinliu, whose struggle to free her people from the British began from an early age. Mentioning the freedom fighters of Manipur and others from the northeast region, the Union minister also reminded the gathering of the Central government’s decision to rename Mount Harriet, the third-highest island peak in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, where Manipur’s Maharaja, Kulchandra Singh, and 22 other freedom fighters were imprisoned after the Anglo-Manipur war (1891).
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs and Microsoft sign MoU on Joint initiative for Digital Transformation of Tribal Schools.
The collaboration seeks to skill educators and students in next-generation digital technologies, including Artificial Intelligence. With a vision to build an inclusive, skills-based economy, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) linked a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Microsoft to support the digital transformation of schools such as Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) and Ashram Schools, among others under the Ministry, at an online event ‘Empowering Youth for Success’. Under affirmative action initiative, Microsoft will make AI curriculum available to tribal students in both English and Hindi at all EMRS schools under the Ministry to skill educators and students in next-generation technologies, including Artificial Intelligence.
Under this programme in the first phase, 250 EMRS schools were adopted by Microsoft, out of which 50 EMRS schools were given intensive training, and 500 master trainers were trained, in the first phase.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs and CBSE jointly launched an online certificate course on Experiential Learning for the 21st Century for EMRS and CBSE teachers
As part of celebrations of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav, the Secretary, Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Shri Anil Kumar Jha and Chairman, CBSE, Shri Manoj Ahuja, jointly launched a certificate course on Experiential Learning for the 21st Century for educators from CBSE and Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRSs) in collaboration with Tata Trusts, CETE, TISS (Centre of Excellence in Teacher Education, Tata Institute of Social Sciences), Mumbai and MGIS (Mahatma Gandhi International School), Ahmedabad.
The programme was deployed for 350 educators in 6 States and the event was attended by Shri Asit Gopal, Commissioner, National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS), an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs. Dr Naval Jit Kapoor, Joint Secretary, Ministry of Tribal Affairs and Mr R. Pavithra Kumar of Tata Trusts were also present, on the occasion.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs and NCERT join hands for the NISHTHA Capacity Building Programme for EMRS Teachers and Principals
To fulfil the long-standing vision of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) and to achieve academic excellence in Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRSs), 120 EMRS teachers and principals from 3 states completed a 40 days’ NISHTHA-National initiative for School Heads and Teachers Holistic Advancement Program’. It was a national flagship program of the NCERT on 19th June 2021. The Capacity Building programme aimed at building competencies among teachers and school principals, additionally, improving the quality of School Education through Integrated Teacher Training.
MoTA recently collaborated with the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), a national apex education body of several programmatic initiatives and interventions and conducted similar programmes across 350 functional EMRS schools pan India.
- Shri Pramod Kumar Shukla, English Lecturer from Eklavya Model Residential School, Chattisgarh, receives National Award for Teachers-2021 from President Sh Ram Nath Kovind on Teacher’s Day.
The Hon’ble President, Shri Ram Nath Kovind, on September 5th 2021, presented the National Teacher Award to 44 talented teachers selected from all over the country on the occasion of Teachers’ Day.

The award was also bestowed upon Shri. Pramod Kumar Shukla, English Lecturer of Eklavya Model Residential School (EMRS), Karpawand, Bastar Chattisgarh. It is the second award in a row for EMRS teachers and holds special significance for Eklavya Model Residential Schools established under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs. In 2020, Smt. Sudha Painuli, Vice Principal, EMRS-Kalsi, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, was felicitated with the award. With the implementation of National Education Policy- 2020, it is believed that greater thrust shall be given to teachers as they gain centre-stage, empowering the teachers to implement the NEP recommendations. It holds direct insinuations to change the facets of EMRSs established for providing quality education to tribal students at the behest of talented and committed teachers.
- 35.2 lakh tribal students disbursed Pre and Post Matric Scholarships through DBT during 2020-21
The Ministry disbursed an amount of Rs. 2500 crores to 35.2 lakh tribal students under Pre and Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme through Direct Benefit Transfer during 2021, amid the Coronavirus pandemic situation to provide essential support for the continuation of education. In this regard, the State’s portals of Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Schemes have been integrated with DBT Tribal Portal and DBT Bharat Portal. Moreover, 331 Universities have been assimilated into this scheme, while an online student verification process has been undertaken to identify and verify the student’s details.
The total Budget Outlay for Pre/Post Matric, National Fellowship and Scholarship, and the National Overseas Scholarship has been upgraded to Rs. 2546 Crores in 2021 from the previous budget outlay of 2013. Over 32, 08,154 students benefitted from these scholarships and the mode of implementation of this scheme remained fully online, to shift from paper-based application to data-based application as well to reduce the release time of the scholarship.
- Union Education Minister and Union Tribal Affairs Minister jointly launched School Innovation Ambassador Training Programme
The Union Education Minister, Shri Dharmendra Pradhan and the Union Minister of Tribal Affairs, Shri Arjun Munda, jointly launched the ‘School Innovation Ambassador Training Program’ for 50,000 school teachers. It aims at training 50,000 School Teachers on Innovation, Entrepreneurship, IPR, Design Thinking, Product development, Idea generation, among others.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs Bags Prestigious SKOCH Challenger Award for “Best Performance In E-Governance” & 3 Gold Awards for Its Initiatives
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) received the coveted “SKOCH Challenger Award”- “Best Performance in e-Governance” today for its various initiatives such as Digital Dashboard and Digital Transparency on its 20+ Online Portals with updated information of its implemented schemes, taken during last year. The Award was received by the Union Minister for Tribal Affairs, Shri Arjun Munda, at the Virtual SKOCH Summit.
The Ministry also received 3 Gold Awards for its initiatives namely “Eco-Rehabilitation of tribal villages through Innovative design in water management using Ice-stupas”, Swasthya: Tribal Health and Nutritional Portal and the Performance Dashboard “Empowering Tribals Transforming India” which were received by Dr Naval Jit Kapoor, Joint Secretary, on behalf of the Ministry.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs bags Award of Appreciation in the 18th CSI SIG E-Governance Awards 2020
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs bagged the prestigious Award of Appreciation in the Project Category-Central Government Entity – in the 18th CSI SIG e-Gov Awards 2020 for their ‘Performance Dashboard Empowering Tribals Transforming India through various ICT initiatives”. The award was received by the Joint secretary of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Dr. Navaljit Kapoor from the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh Shri Yogi Adityanath in Lucknow.
- Tribal women making Rakhis with seeds of indigenous trees under Vruksha Bandhan Project
In a unique initiative Ministry of Tribal Affairs in partnership with The Art of Living Foundation, Aurangabad, and Maharashtra launched Vrushka Bandhan Project where 1100 tribal women created Rakhis for Raksha Bandhan with seeds of indigenous trees, which is a unique contribution to increasing forest cover & combating climate change.
The Rakhis were made of indigenous seeds stuck on naturally dyed, soft indigenous, non-toxic, biodegradable cotton. Once used, the seeds can be sown in soil, thereby benefiting the environment. It is expected that thousands of trees would be planted under this project and project will provide employment to tribal women associated with the project.
- Tribal Affairs Ministry and AIIMS organized workshop for NGOs for mission of Sahi Poshan-Desh Roshan as part of POSHAN MAAH


A workshop for Non-Governmental Organizations on Nutrition and Health was organized by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs on 09th September, 2021, as part of its POSHAN MAAH activities. The purpose of the workshop was to closely associate NGOs working with Ministry of Tribal Affairs in the mission of Sahi Poshan-.Desh Roshan. The workshop was attended by more than 70 NGOs who are working in the health sector in tribal areas.
- 86 ST Entrepreneurs from Southern States honoured as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav Week Celebrations of Tribal Affairs Ministry
In a bid to promote entrepreneurship amongst the tribal community and encourage successful entrepreneurs, a grand event was organized by the National Scheduled Tribes Finance and Development Corporation (NSTFDC) and Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India honoured tribal entrepreneurs on 22nd November 2021 at Visakhapatnam in association with TRICOR-Andhra Pradesh
- Tribal Affairs Ministry has taken up several initiatives to promote leadership qualities and talent among tribal youth
GOAL (Going Online as Leaders) is a joint initiative of Ministry with Facebook for digitally-enabled mentorship and empowering tribal youth to become leaders in their area of interest. Through the GOAL initiative, renowned people from the industry, arts, politics, business etc., known for their leadership skills or roles, are mobilized to personal mentor tribal youth through a digital medium. GOAL program has so far covered 23 States / UTs.
Ministry of Tribal Affairs continuously strives for fostering partnerships with reputed organizations: working for the welfare of tribes like Microsoft, Art of Living Foundation, Tata Foundation, and SECMOL aimed at taking the project with community participation and for creating awareness about leadership among tribal youth.
- One Day National Conference on Provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to the Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA) organised to celebrate 25th year of PESA
One of the themes of Amrit Mahotsav is the ‘whole of Government approach’ and ‘Jan Bhagidari’. Taking this into consideration, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs planned several activities during this period both at the National as well as the State Level.
PESA is a significant Act for the welfare of the tribal communities. Officials of the State and Public representatives were asked to visit tribal regions and comprehend the issues of the Tribal at the grassroots level. During the gathering, it was accentuated that safeguarding the culture of the tribal communities is a necessary measure, to be transparent with the tribals and show them the ray of development under rapidly evolving scenarios. Endeavors were made toward this path in many states; different exercises were embraced under PESA in Maharashtra resulting in the economic empowerment of tribals.
- National Aadi Mahotsav held in Dilli Haat, INA, New Delhi– A Celebration of Tribal Culture, Crafts and Commerce
The National Aadi Mahotsav was held at Dilli Haat, INA, New Delhi, from the 1st to the 15th February 2021. It celebrated several aspects of tribal culture that evinced a lot of interest and witnessed much footfall in the first place. The festival was an attempt to familiarize the people with the rich and diverse craft, the culture of the tribal communities across the country in one place.
The fortnight-long National Tribal Festival witnessed the participation of thousands of tribal artisans, chefs, artists and cultural troupes from 25 states across the country. The rich tribal culture was evident in the forms of rare tribal handicrafts, handloom and natural products, tribal cuisines as they were exhibited in about 200 stalls. The Aadi Mahotsav succeeded in winning the hearts of the residents of Delhi and witnessed heavy footfall over 15 days and the sales registered. It observed tribal artisans register approx. Rs 4 Crore in direct sales over the past fortnight. Moreover, a purchase order worth Rs 8 Crores was placed by TRIFED; leading to a total of approx. Rs 12 Crores in business transactions for the tribals participating in this festival. The Aadi Mahotsav was in its entirety a celebration of the spirit of tribal life – crafts, culture and cuisine.
- Tribes India – Aadi Mahotsav
As India is celebrating the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav, Aadi Mahotsav from 16th November to 30thwas organised in Dili Haat.

With more than 200 stalls from across the country and about 1000 artisans and artists participating with their unique stories, the AadiMahotsav is a way to draw the Adivasis into the mainstream. Showcasing traditional art and handicrafts, and the cultural heritage of the country, this festival connects the tribal artisans with larger markets and brings to focus the diversity and richness of the tribes of India.

The Aadi Mahotsav is a mini-India where the exquisite craft traditions of tribal artisans – weavers, potters, puppeteers, and embroiders – are all in one place. With a wide range of artefacts like paintings be it in the Warli style or Pattachitras; jewellery handcrafted in the Dokra style to bead necklaces from the Wancho and Konyak tribes to the famous Toda embroidery from the South; from virgin coconut oil of the Nicobar Islands to multi-flavoured Nutra-beverages of north-east; from colourful puppets and children’s toys to traditional weaves such as Dongri shawls, Bodo weaves, Kota Doria from Rajasthan; iron craft from Bastar to bamboo craft and cane furniture; pottery such as blue pottery and Longpi pottery from Manipur, the festival is a feast for the senses.
- Shri Arjun Munda, Minister of Tribal Affairs virtually launched the nationwide campaign “COVID Teeka Sang Surakshit Van, Dhan aur Uddyam” to accelerate the pace for COVID vaccination among tribals in India.
The campaign was launched to leverage the 45,000 Van Dhan Vikas Kendras (VDVK) of the Tribal Co-operative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED), a national level cooperative body under the administrative control of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India.
- M/o Tribal Affairs and Goa Government Jointly Launch Shramshakti Digital Data Solution Tomorrow for Migrant Workers and Tribal Migrant Cell
In a move that would effectively help in the smooth formulation of State and National level programs for migrant workers, the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) launched “Shram Shakti”, a National Migration Support Portal and Shram-Saathi, a training manual for migrant workers in Goa. To facilitate and support approximately 4 lacs migrants who come from different States to Goa, the Chief Minister of Goa will also launch a dedicated Migration cell in Goa. MoTA has also sanctioned Tribal research Institute, Tribal Museum, Van Dhan Kendras and Tribal Lok Utsav in Goa.
- Tribal Affairs Minister Shri Arjun Munda launched ‘Adi Prashikshan Portal’ and 3 -Day Online Capacity Building Programme for ST PRI Members
Hon’ble Union Minister of Tribal Affairs, Shri Arjun Munda, launched the ‘ADI PRASHIKSHAN’ portal and inaugurated a three-day training programme on “Capacity Building Training of Master Trainers for ST PRI Members” as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav in New Delhi.
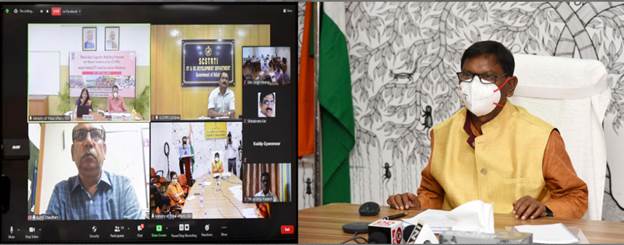
The Adi Prashikshan portal developed by the Ministry acts as a Central Repository of all training programs conducted by Tribal Research Institutes (TRIs), different divisions of Ministry, National Society for Education of Tribal Students (NESTS), Centre of Excellence funded by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and National Tribal Research Institute.
- M/o Tribal Affairs organised the second National Conclave on Sickle Disease in India on World Sickle Cell on 19th June, 2021 Unmukt project to eliminate Sickle Cell Disease launched
To commemorate World Sickle Cell Disease Day on 19th June 2021, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MOTA) organized the Second Online National Conclave on ‘Sickle Cell Disease in India’, in partnership with FICCI, Novartis, Piramal Foundation, Apollo Hospitals, NASCO and GASCDO.The event brought together a group of experts on Sickle Cell Disease across India to deliberate on recent advances in Sickle Cell Disease management-ranging from early diagnosis to the latest medicines and advances in the treatment of the disease.

Shri Arjun Munda, Union Minister and Renuka Singh Sauta flagged off mobile vans under the Unmukt project for strengthening screening and timely management of SCD in Khunti district of Jharkhand and Kanker in Chhattisgarh, two tribal districts with a high prevalence of sickle cell disease among tribals.
- Tribal Health Collaborative ‘Anamaya’: A Multi Stakeholder Initiative to enhance Tribal Health and Nutrition launched
Anamaya, the Tribal Health Collaborative, was launched by Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare Dr Harsh Vardhan and Union Minister of Tribal Affairs, Shri Arjun Munda, at a function in New Delhi . The Collaborative is a multi-stakeholder initiative of the Tribal Affairs Ministry supported by the Piramal Foundation and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF). It will converge efforts of various Government agencies and organisations to enhance the health and nutrition status of the tribal communities of India.
- Joint Communication for more effective implementation of the Forest Rights Act signed by Environment and Tribal Affairs Ministries
The Forest Rights Act (FRA) 2006 recognizes the rights of the forest-dwelling tribal communities and other traditional forest dwellers. These communities are dependent on forest resources for a variety of needs, including livelihood, habitation and other socio-cultural needs.
A “Joint Communication” was signed by Shri R.P. Gupta, Secretary, Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC), and Shri Anil Kumar Jha, Secretary, Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), in the presence of Minister of Environment, Shri Prakash Javadekar and Minister of Tribal Affairs, Shri Arjun Munda.
The Joint Communication, addressed to all Chief Secretaries of States/UTs, pertains to more effective implementation of the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006 and for harnessing the potential for livelihood improvement of the Forest Dwelling Scheduled Tribes (FDSTs) and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (OTFDs).
- Shri Arjun Munda, Union Minister for Tribal Affairs inaugurates New Building complex for the Tribal Cultural Research & Training Mission (TRI), Andhra Pradesh as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav
Union Minister of Tribal Affairs, Sh. Arjun Munda; MoS Tribal Affairs, Renuka Singh Saruta, and Dy. Chief Minister & Minister for Tribal Welfare, Andhra Pradesh, Smt.Pamula Pushpa Srivaniji virtually inaugurated the New Building complex for the Tribal Cultural Research and Training Mission (TRI) of Andhra Pradesh on 15th August 2021 as a part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav India @ 75.
- Measures undertaken by the Government to improve the livelihood of Tribals during COVID situations
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs provided funds to the State Governments based on their proposals for undertaking various livelihood activities, including agriculture, horticulture, animal husbandry, fisheries and other non-farm based livelihood activities etc. under the schemes ‘Special Central Assistance to Tribal Sub-Scheme (SCA to TSS)’, ‘Development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)’ and ‘Grants under Article 275(1)’ during 2020-21. An amount of Rs. 587.47 crore was approved/sanctioned by various State Governments for launching various livelihood activities.
Further, funds to the tune of Rs. 12355.43 crore have been provided as Scheduled Tribe Component (STC) by the other Central Ministries / Departments under livelihood related schemes during 2020-21 and 2021-22.
- Institutional Support for Development and Marketing of Tribal Products/Produce:
- Under the scheme, TRIED has been promoting E-Commerce sale of tribal products from its own portal http://www.tribesindia.com and also present on all major e-commerce portals like Amazon, Snapdeal, Flipkart, Paytm, and GEM.
- TRIFED has made the online sales of Rs. 99.74 lakhs in financial year 2020-21. During the current financial year 2021-22, TRIFED has made the sale of Rs.127.54 lakhs (Upto 30.11.2021).
- TRIFED has established a network of 145 Outlets i.e. 97 own Sales outlets, 33 outlets on consignment sale and 15 franchise outlets located across the country as on 30.10.2021.
- The total number of suppliers/producers empanelled with TRIFED as on 31.10.2021 is 2915.
- Sale of tribal products by TRIFED during 2019-20 – Rs. 40.30 cr, 2020-21 – Rs. 29.63 cr and 2021-22 (as on 30.10.2021) – Rs. 18.43 cr.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) for Minor Forest Produce (MFP) SCHEME:
- MSP for majority of Minor Forest produce have been increased.
- 37 new items under the MSP for MFP scheme list from 2020-21.
- No. of MFP under MSP scheme increased from 50 to 87 during 2020-21.
- Procurement of MFPs under MSP for MFP scheme by States from GoI funds is Rs. 317.89 Cr. since the implementation of the scheme.
- Van Dhan Vikas Karyakaram:
- Under the scheme of ‘MSP for MFP’ Van Dhan Vikas Kendra Clusters (VDVKCs) act as common facility centres for procurement cum value addition to locally available Minor Forest Produce.
- Rs. 254.64 cr. released to TRIFED in last three years for setting up Van Dhan Vikas kendra Clusters (VDVKCs).
- 3110 VDVKCs have been sanctioned till date since its inception in 2019-20 benefitting 9.28 lakh MFP gatherers of more than 52000 SHGs.
- Equity Support to NSTFDC/STFDCs:
- NSTFDC extends concessional loans to the eligible Scheduled Tribe persons for undertaking any income generation activities/ self-employment through its implementing agencies.
- Rs. 748.75 cr have been disbursed by NSTFDC in the last three years (2019-20 to 30.11.2021) to 4.04 lakh tribal beneficiaries under its five schemes.
- NSTFDC has signed MoU with KVIC to act as implementing agency under PMEGP scheme. The MoU aims at providing concessional loans to tribal entrepreneurs seeking financial assistance through banks and SCAs and the ST beneficiaries will get back ended subsidy up to 35% of the unit cost.
****











































You must be logged in to post a comment.